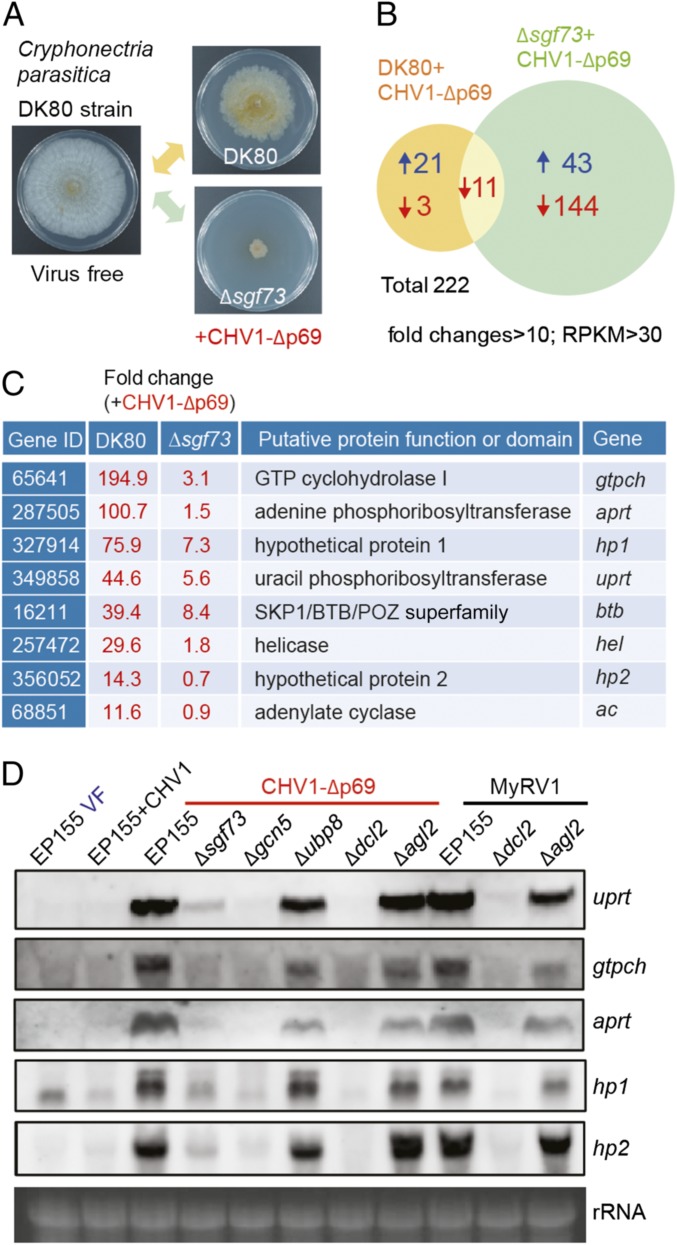
Fig. 1.
The role of the SAGA complex and DCL2 in gene transcriptional up-regulation upon viral infection. (A) Colony morphology of the virus-free DK80 and the CHV1-Δp69–infected DK80 and Δsgf73 mutant C. parasitica strains. The fungal strains were grown on PDA plates for 7 d and photographed. (B) Transcriptomic analysis showing the number of genes with altered transcript expression in the DK80 and Δsgf73 strains upon CHV1-Δp69 infection. Transcript levels were compared between virus-free DK80 and each of CHV1-Δp69–infected DK80 and Δsgf73. (C) List of genes with highly induced expression in DK80 but not in Δsgf73 following CHV1-Δp69 infection. Gene IDs were obtained from the JGI Genome Portal (https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Crypa2/Crypa2.home.html). (D) RNA blotting analysis of the uprt, gtpch, aprt, hp1, and hp2 gene transcripts in the wild-type strain (EP155) and the SAGA complex (Δsgf73, Δgcn5, and Δubp8)- and RNA silencing (Δdcl2 and Δagl2)-related fungal mutant strains infected with CHV1, CHV1-Δp69, and MyRV1, or virus-free (VF). The RNA gel was stained with ethidium bromide, and 28S rRNA is shown as a loading control (rRNA) in this and subsequent figures.