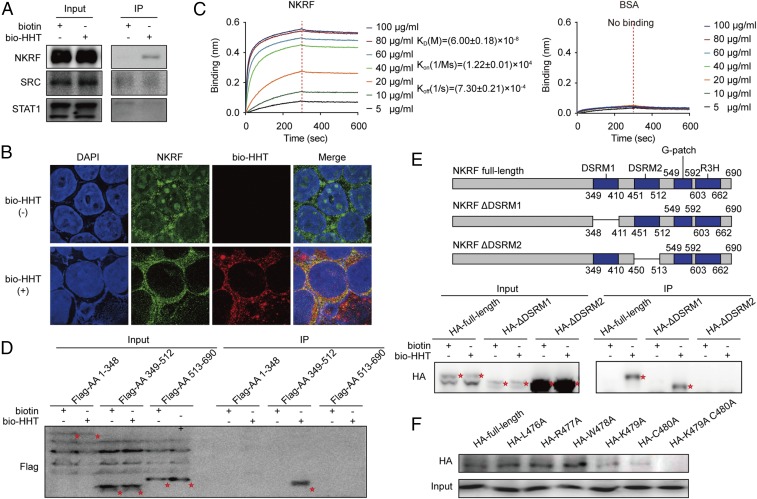
Fig. 3.
Mapping the direct binding site of NKRF protein to HHT. (A) Validation of the binding of SRC, STAT1, and NKRF with bio-HHT by SA agarose affinity assay. (B) Colocalization of NKRF with biotin-HHT analyzed by immunofluorescence staining. (Magnification: 630×.) (C) BLI analysis of the binding affinity between HHT and increasing concentrations of 6× His-NKRF. BSA served as a negative control. (D) Binding effect between bio-HHT and the full-length or truncated NKRF constructs (HA-labeled) detected by immunoprecipitation assay. Protein bands are highlighted by red asterisks. (E, Upper) Schematic representation of NKRF deletion mutants. (E, Lower) Binding effect between bio-HHT and the full-length or deleted NKRF mutants (HA-labeled) detected by immunoprecipitation assay. Protein bands are highlighted by red asterisks. (F) Effects of NKRF amino acid 479 and 480 substitutions on binding of NKRF to HHT.