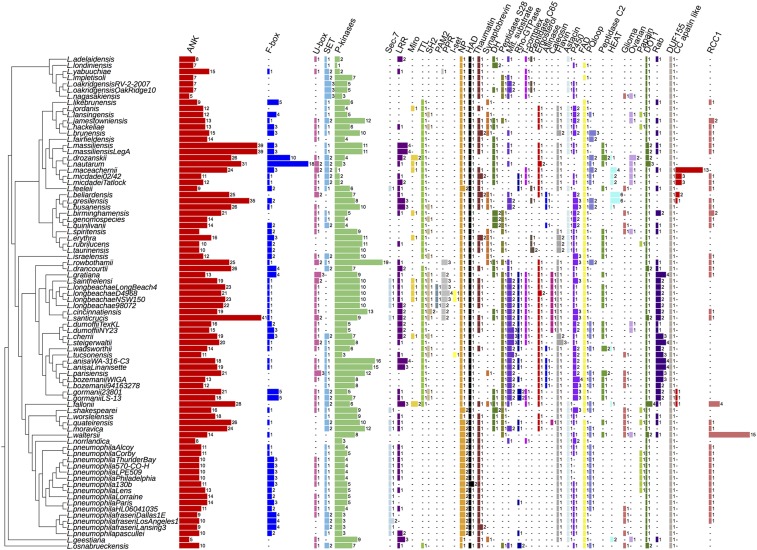
Fig. 2.
Eukaryotic domains have a diverse distribution within the genus Legionella, suggesting multiple acquisition events. The number and distribution of the 41 most frequently identified eukaryotic motifs within the genus Legionella are shown. Numbers represent the number of proteins containing this eukaryotic motif. ANK, ankyrin; Astacin, peptidase M12A astacin; C/C, clathrin/coatomer adaptor adaptin-like; DH, Dbl homology domain; DOT1, histone methylation DOT1; Ergosterol, ergosterol biosynthesis; FAD, cytokinin dehydrogenase 1 FAD/cytokinin binding domain; F-box, F-box domain; Flavin, flavin monooxygenase-like; Glioma, leucine-rich glioma-inactivated EPTP repeat; HAD, HAD-superfamily hydrolase; I-set, Ig I-set; LLR, leucine rich repeats; Miro, mitochondrial Rho domain; Mit. substrate, mitochondrial substrate/solute carrier; NP, nucleoside phosphatase gda1/cd39; Ovarian, ovarian tumor otubain; P450, cytochrome_P450; PAM2, ataxin-2 C-terminal; Papain, peptidase C1A papain C-terminal; Peptidase C2, calpain catalytic domain; Peptidase C65, peptidase C65 otubain; P-kinases (protein kinases); PPR, pentatricopeptide repeat; PQloop, PQ loop repeat; Rab, Rab small GTPases; RCC1, regulator of chromosome condensation; Rho-GTPase, Rho-GTPase domain; Sec-7, Sec-7 domain; SET, SET domain; SH2, Src homology 2; T-complex, T-complex 10/11; TTL, tubulin-tyrosine ligase; U-box, U-box domain.