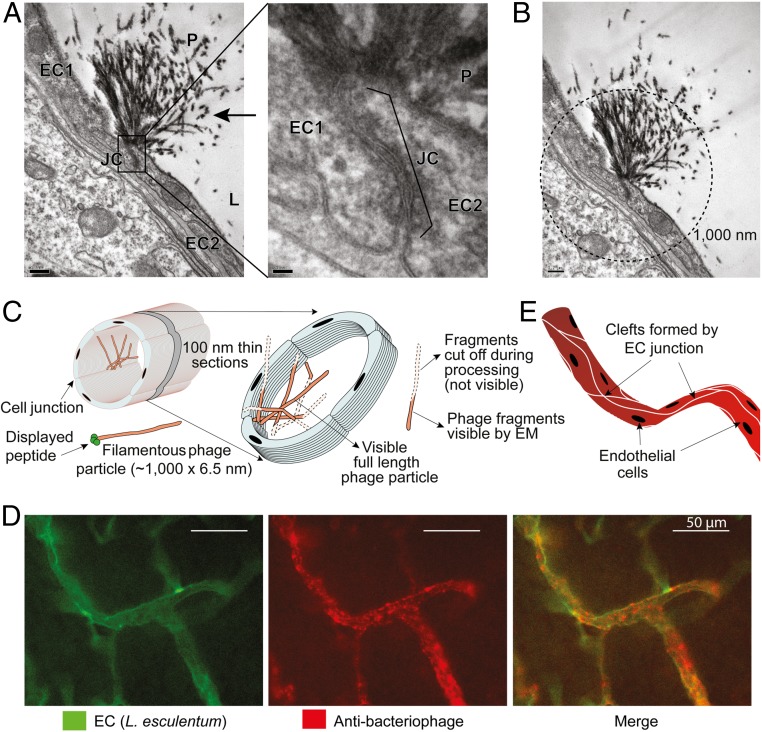
Fig. 3.
CFFWKFRWMC peptide targets brain endothelial junctions. (A) TEM images of brain from a mouse receiving i.v. targeted CFFWKFRWMC-displaying phage (1010 TU) (100-nm section). Left (magnification 10,000×) shows lumen (L) and junction (JC) of two endothelial cells (EC1 and EC2). The typical morphology of filamentous phage (P) is indicated (arrow). Right depicts a higher magnification (60,000×) highlighting the junction between two endothelial cells. (Scale bars: 200 nm.) (B) Calculated length of the phage tufts. Circle in dashed lines indicates 1,000-nm diameter centered at the base of the endothelial junction. (Scale bar: 20 nm.) (C) Schematic illustration of the observed phage tufts in 100-nm thin sections. (D) Immunofluorescence detection of targeted CFFWKFRWMC-displaying phage bound to cell clefts formed by junctions and branches of endothelial cells of blood vessels in the brain. (E) Schematic illustration of the clefts of endothelial cells formed along the longitudinal axis of the blood vessels.