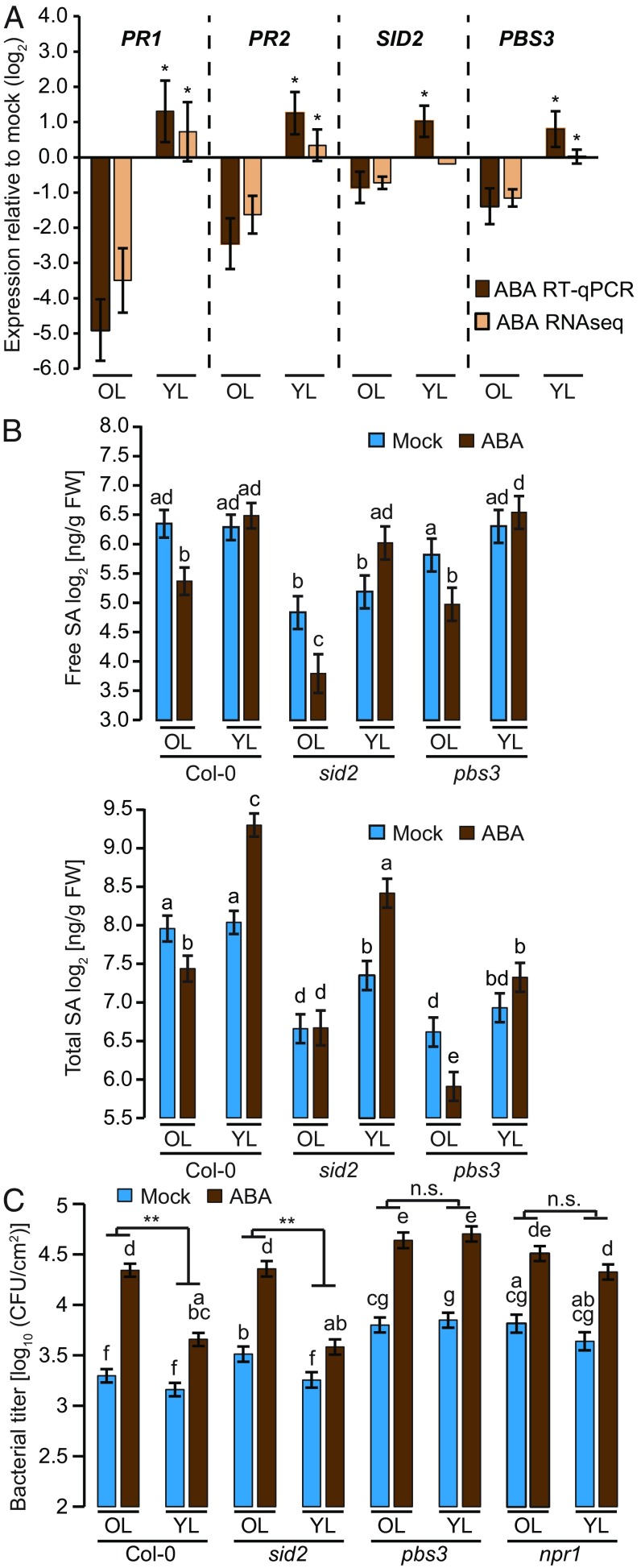
Fig. 3.
PBS3 protects young leaves from ABA-triggered immune suppression. (A) The expression changes of PR1, PR2, SID2, and PBS3 in old leaves (OL) and young leaves (YL) of 4–5-wk-old Col-0 plants 48 h after 500 µM ABA spray compared with mock in RNA-seq and quantitative RT-PCR. Data represent means ± SEM of three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences in young compared with old leaves (*P < 0.05, two-tailed Student’s t tests). (B) Free and total SA amounts in old and young leaves of 4–5-wk-old Col-0, sid2, and pbs3 plants 48 h after spray with 500 µM ABA or mock. Data represent means ± SEM calculated from three biological replicates by using a mixed linear model. Different letters indicate significant differences (adjusted P < 0.05). (C) Old and young leaves of 4–5-wk-old Col-0, sid2, pbs3, and npr1 plants were infiltrated with Pto hrcC− (OD600 = 0.0002) 24 h after 500 µM ABA spray or mock. Bacterial growth was measured at 2 days postinoculation. Data represent means ± SEM calculated from three independent experiments, each with at least five biological replicates, by using a mixed linear model. Different letters indicate significant differences (adjusted P < 0.005; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, two-tailed Student’s t tests). n.s., not significant.