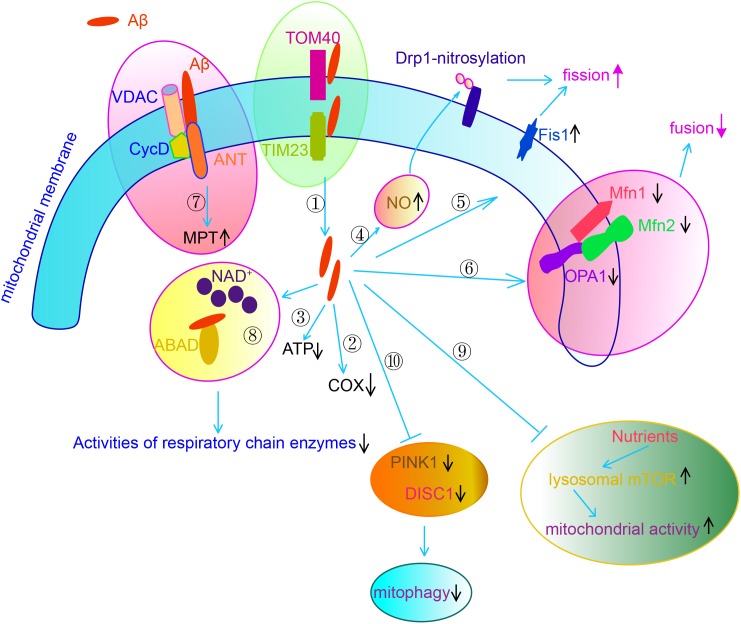
FIGURE 3.
Aβ causes mitochondrial dysfunction via multiple mechanisms.  Aβ is imported to the mitochondria through interacting with TOM40 and TIM20, eventually localizing cross mitochondrial membrane.
Aβ is imported to the mitochondria through interacting with TOM40 and TIM20, eventually localizing cross mitochondrial membrane.  Aβ decreases COX activity.
Aβ decreases COX activity.  Aβ decreases ATP generation via binding to ATP synthase subunit α.
Aβ decreases ATP generation via binding to ATP synthase subunit α.  Aβ increases NO generation, which results in S-nitrosylation of DLP.
Aβ increases NO generation, which results in S-nitrosylation of DLP.  Aβ increases the expression of Fis1. Through
Aβ increases the expression of Fis1. Through  and
and  , Aβ enhances mitochondrial fission.
, Aβ enhances mitochondrial fission.  Aβ decreases the expression of Mfn1/2 and OPA1, through which Aβ suppresses mitochondrial fusion.
Aβ decreases the expression of Mfn1/2 and OPA1, through which Aβ suppresses mitochondrial fusion.  Aβ regulates mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) via forming an interacting complex with ANT, cyclophilin D (Cyc D) and VADC, the core components of MPTP.
Aβ regulates mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) via forming an interacting complex with ANT, cyclophilin D (Cyc D) and VADC, the core components of MPTP.  Aβ interacts with ABAD, preventing NAD+ to ABAD, thereby changing MTP and decreasing the activities of RC.
Aβ interacts with ABAD, preventing NAD+ to ABAD, thereby changing MTP and decreasing the activities of RC.  Aβ suppresses nutrients induced mitochondrial activity through regulation mTOR activity.
Aβ suppresses nutrients induced mitochondrial activity through regulation mTOR activity.  Aβ impairs mitophagy through downregulation of DISC1 and PINK1.
Aβ impairs mitophagy through downregulation of DISC1 and PINK1.