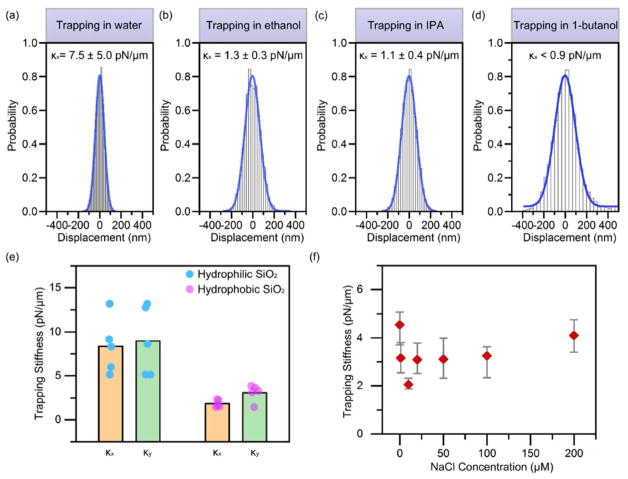
Figure 3. Effects of solvent, particle hydrophilicity and ion concentration on opto-thermophoretic trapping of colloidal particles.
(a–d) Measured histograms of particle displacement and the corresponding trapping stiffness (x direction) for 500 nm PS spheres in water, ethanol, IPA and 1-butanol. (e) Measured trapping stiffness for 1 μm hydrophilic and hydrophobic silica (i.e., SiO2) particles in water. The dots indicate the values of different particles. The columns indicate the average values. (f) Measured trapping stiffness for 1 μm PS spheres in IPA as a function of NaCl concentration. A focused laser beam with a diameter of ~ 520 nm and an optical power of ~ 0.5 mW was illuminated onto the optothermal substrate with a thin chamber of (a–d, f) 20 μm in depth and (e) 120 μm in depth. Standard deviations (a–d) and error bars (f) of the trapping stiffness were obtained by tracking 5–6 different particles.