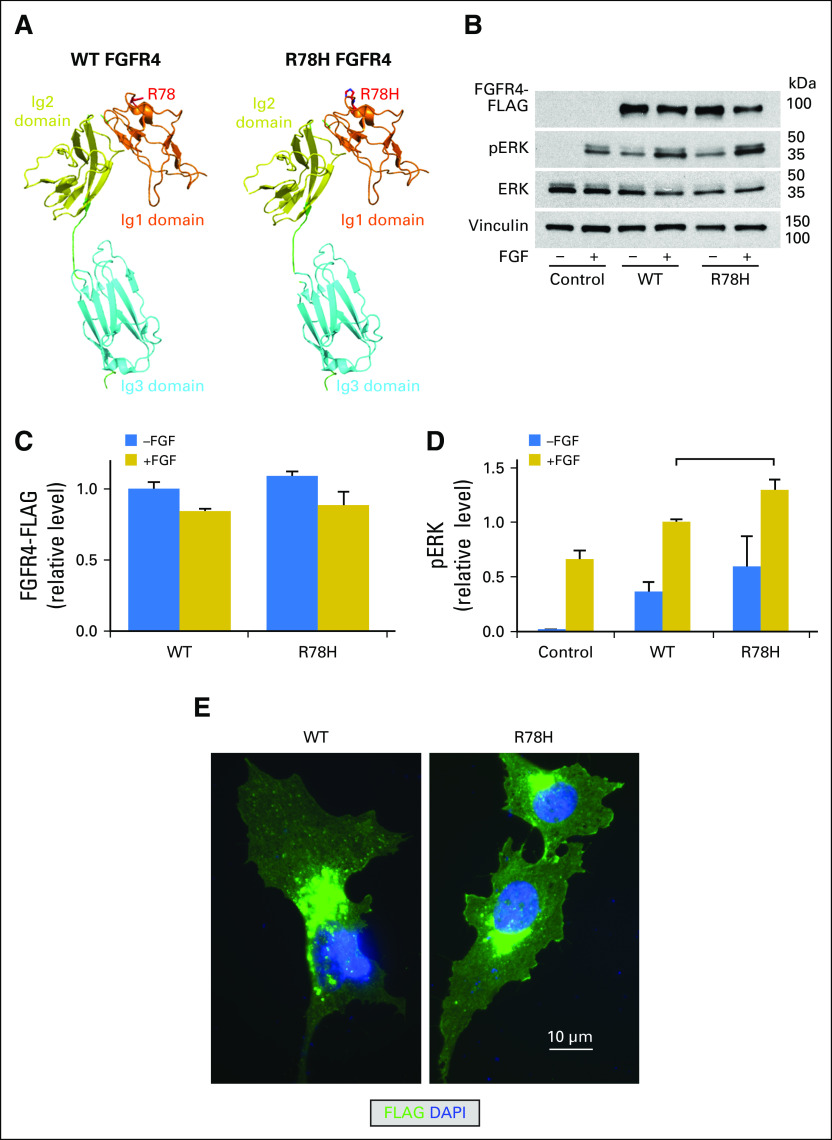
Fig 2.
Functional evaluation of FGFR4 variants of unknown significance (VUSs). (A) PyMOL modeling of wild-type (WT; left) and R78H (right) FGFR4. KMCH-1 cells were transfected to express FLAG-tagged WT and R78H FGFR4, or vector only (control). After 1 day, the cells were incubated at 37°C with and without FGF2 in 0.1% bovine serum albumin/DMEM overnight. Right panel: After 1 day, the cells were incubated with and without 20 ng/mL FGF2 in 0.1% bovine serum albumin/DMEM for 16 hours at 37°C. (B) Cell samples were then lysed and subjected to Western blot analysis. Total ERK and vinculin are shown as loading controls. (C) Quantitation of FGFR4 in Western blots (n = 5). Values are mean ± SE normalized to WT (−FGF2) levels. (D) Quantitation of phospho-ERK (pERK) in Western blots (n = 5). Values are mean ± SE normalized to WT (+FGF2) levels. Bracket indicates groups within treatment types (−FGF or +FGF) among FGFR4-transfected samples that were significantly different (P < .05) from each other in two-tailed t tests. (E) HuCCT-1 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged WT and R78H FGFR4 for 2 days and then processed for immunofluorescence by using an anti-FLAG antibody. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Ig1, immunoglobulin-like domain 1.