Fig. 2.
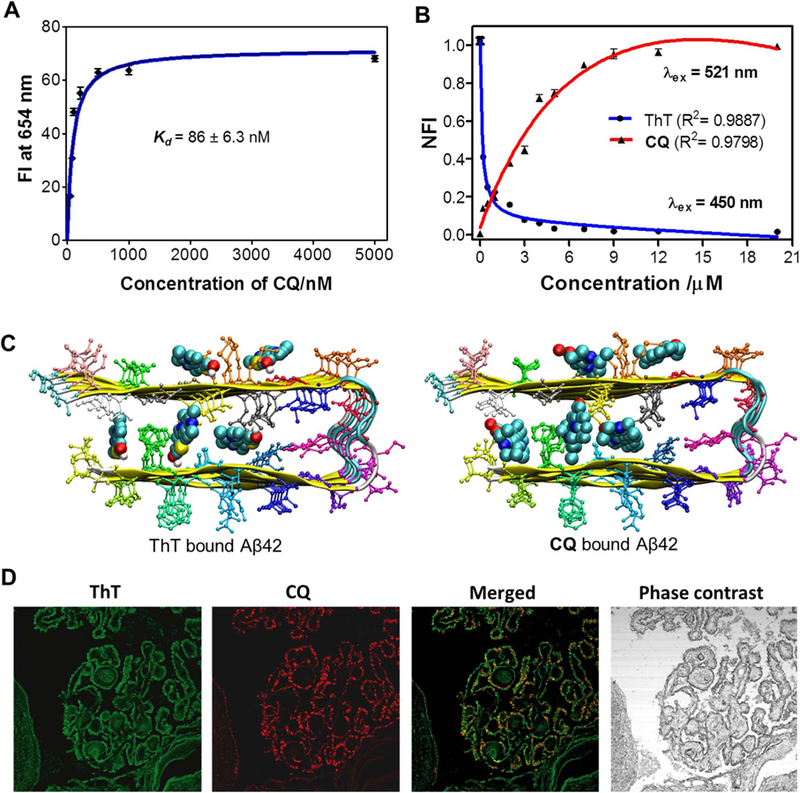
A) Plot of the fluorescence intensity (FI) as a function of the concentration of CQ(0.052, 0.078, 0.102, 0.210, 0.5, 1 and 5 mM) in the presence of Aβ42fibrillar aggregate (10 μM) in PBS (10 mM, pH = 7.4). B) Change in fluorescence of ThT (λex at 450 nm; fluorescence measured at 483 nm) and CQ (λex at 521 nm; fluorescence measured at ~654 nm) upon titrating CQ to ThT/Aβ42fibrillar aggregate complex (ThT, 10 µM/Aβ42fibrils, 20 µM). C) Binding sites available for ThT and CQ within Aβ42 fibril (12 mer assembly). D) CQ stains multiple amyloid plaque structures with specificity. Dual staining of human brain cross sections using CQ and ThT (100 nM CQ: 1.57 mM ThT). While the ThT appears to stain many different amyloid aggregates, the CQ produces lower background fluorescence and shows extreme selectivity for amyloid angiopathy. This is evident by the ring shaped structures localized at the outer wall of the tissue. Each experiment was repeated three times (n = 3) and error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of the fluorescence measurement. NFI = Normalized fluorescence intensity.
