Extended Data Figure 4. Key structural features and comparisons that help sort out the sequence of the seven conformational states.
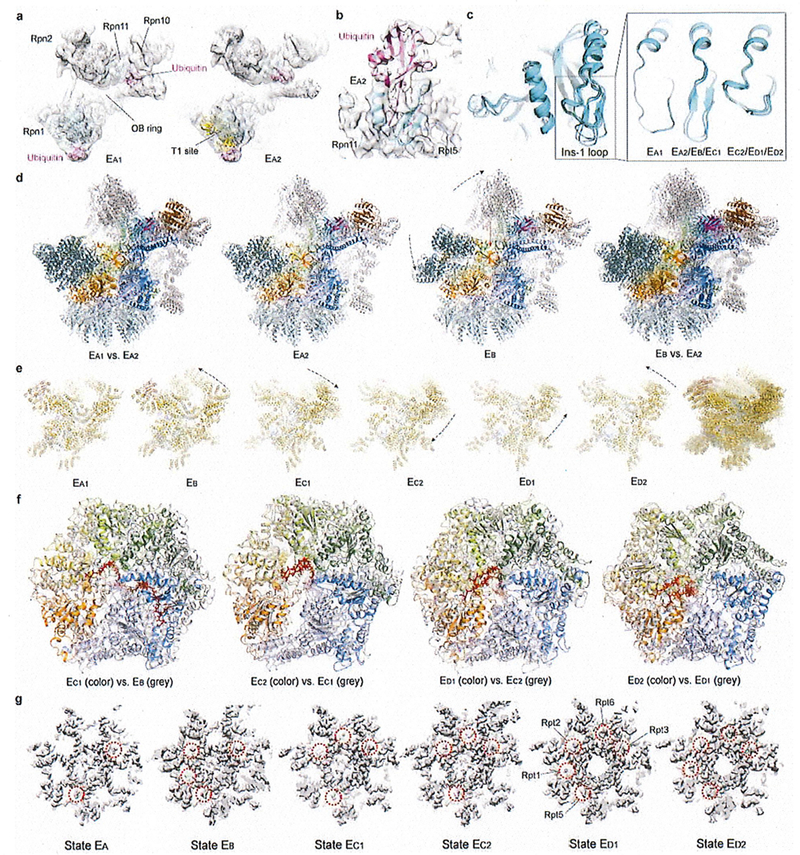
(a) The ubiquitin densities in state EA1 (left) and EA2 (right). The T1 site is labelled by fitting the yellow cartoon representation of the NMR structure (PDB ID 2n3u) of Rpn1 T1 element in complex with two ubiquitins into our density, showing the ubiquitin on Rpn1 is bound to a site very close to the T1 site17. The density maps are low-pass filtered to 8 Å to show the ubiquitin features clearly, due to the lower local resolution of the ubiquitin density in these maps. (b) The ubiquitin-Rpn11-Rpt5 interface observed at high resolution in state EB is also observed in state EA2, albeit at somewhat lower local resolution. The EA2 density is shown as a transparent surface. (c) Comparison of the Insertion-1 loop of Rpn11 in different states. (d) Comparison of the RP structures between EA and EB. (e) Comparison of the lid subcomplex conformations among all states. (f) Comparison of ATPase ring structures between two successive states. The structures are aligned together against their CP in d-f. (g) Comparison of the RP-CP interface and the Rpt C-tail insertions into the CP surface pockets in different states. The ctyo-EM densities of the RP-CP interfaces are shown as a grey surface representation.
