Figure 5. Mechanism for processive substrate translocation driven by a complete cycle of ATP hydrolysis.
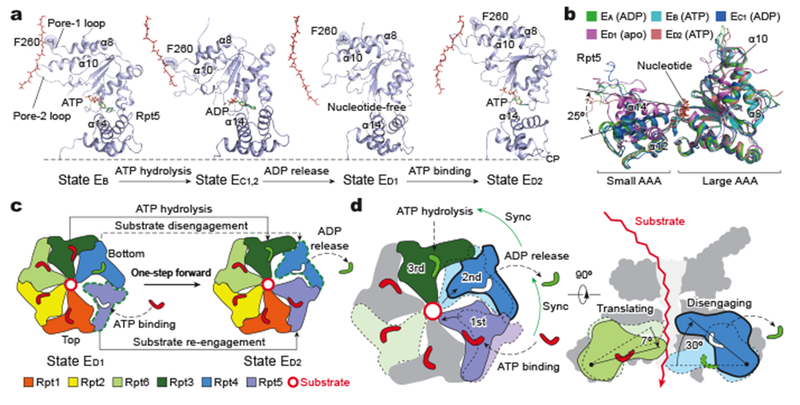
a, Side-by-side comparison of Rpt5 conformations in four sequential states that cover a complete cycle of ATP hydrolysis and exchange in Rpt5. The structures are aligned against the CP to show their conformational changes relative to the CP gate. Phenylalanine-260 of the pore-1 loop is shown in stick representation and highlighted with transparent sphere representation. Substrate is shown in red in stick representation. b, Superposition of Rpt5 structures from five distinct states aligned against the large AAA subdomain shows that Rpt5 assumes two major conformations between apo-like and nucleotide-bound states. c, Schematic representation of ATP hydrolysis and nucleotide exchange required to implement the transition from ED1 to ED2. d, Schematic illustrates mechanism for processive substrate translocation. Synchronization of nucleotide processing in three adjacent ATPases, i.e., ATP binding, ADP release and ATP hydrolysis (left), creates differential vertical rotations in each ATPase that cooperatively translate the substrate (right).
