Fig 4. elgi localization and interaction with Dachs, and elgiCS phenotypes.
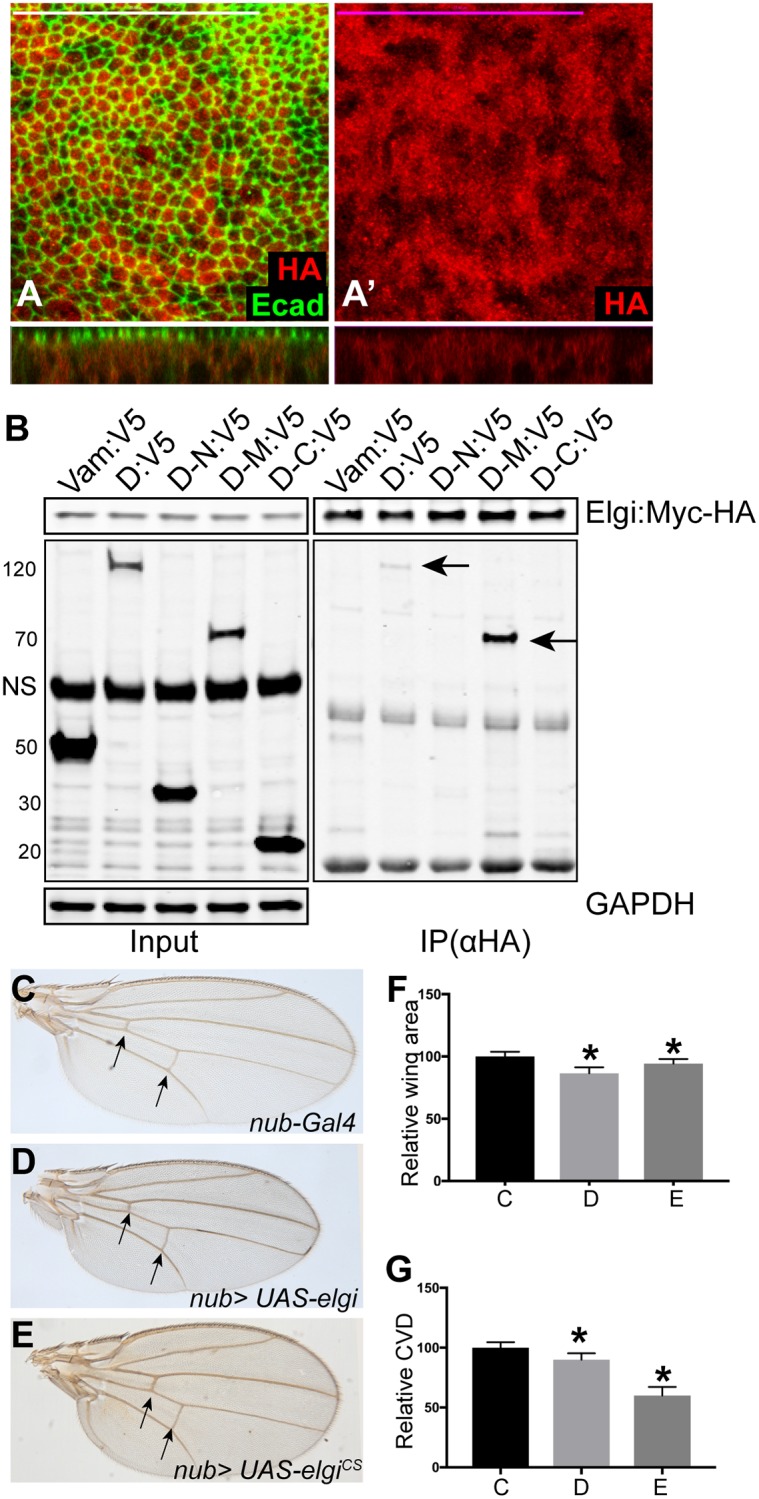
(A, A’) Horizontal apical sections (above) and vertical sections (below) of wing imaginal discs expressing nub-Gal4 UAS-elgi-MYC-HA and stained with anti E-cad (green) and anti HA (red) antibodies showing diffuse cytoplasmic localization of Elgi. Scale bar is 33.0 μm. (B) Western blot showing results of co-immunoprecipitation experiments on proteins co-expressed in S2 cells. V5-tagged Vam, Full length Dachs (D:V5), Dachs N terminus(D-N:V5), Dachs Middle domain (D-M:V5) or Dachs C terminus (D-C:V5) were co-expressed with full length Elgi-MYC-HA, and complexes were precipitated using Ezview red anti HA affinity resin and immunoblotted with Rabbit anti V5 and Rabbit anti HA antibodies. GAPDH was used as a control for loading and transfer in the input lanes. Arrows point to the co-immunoprecipitated bands. NS: non-specific (C-E) Adult male wings from flies expressing nub-Gal4 (control) (C), nub-Gal4 UAS-elgi (D) and nub-Gal4 UAS-elgiCS (E). Arrows point to the crossveins. (F-G) Histograms of relative wing areas (normalized to the average wing area of control wings) (F) and ratios of CVD to wing length, (normalized to the average CVD to wing length ratio of control wings) (G) in flies of the genotypes in panels C-E, as indicated. Data are shown as mean ± SD from measurements of 12 wings per genotype. *P<0.001, (Student’s t test between control and the other genotypes).
