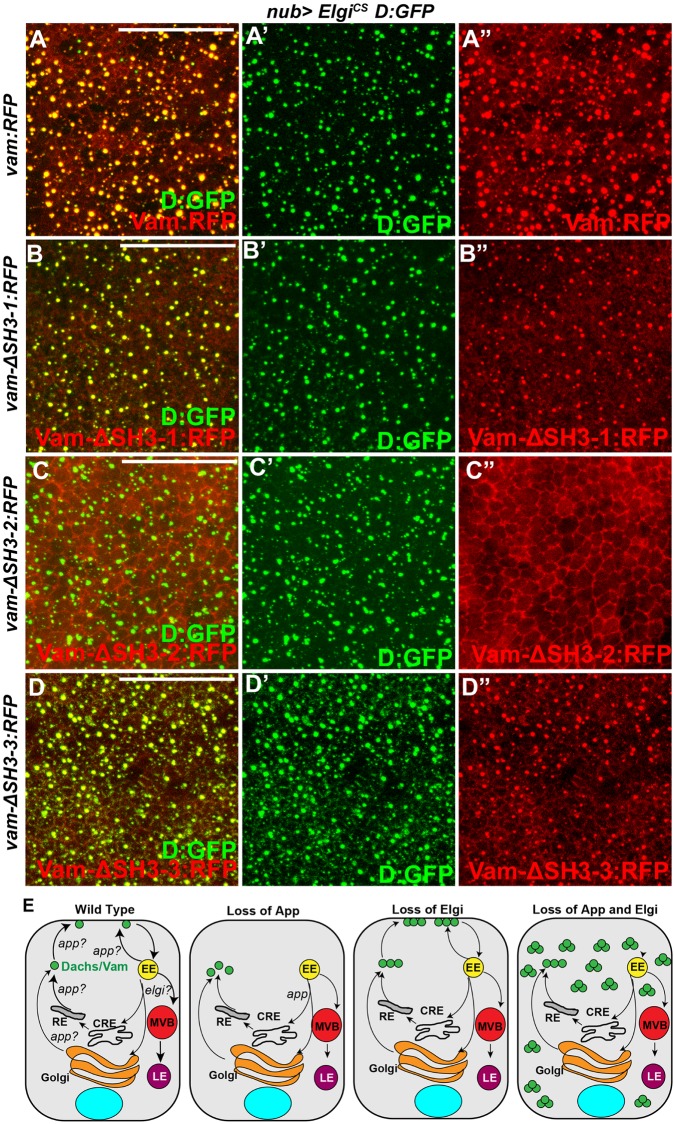
Fig 8. elgiCS affects Dachs rather than Vam.
(A-D) Horizontal apical sections of wing imaginal discs expressing nub-Gal4 UAS-elgiCS D:GFP along with either UAS-vam-RFP (A, A', A”), or UAS-vam-Δ-SH3-1-RFP (B, B', B”), UAS-vam-Δ-SH3-2-RFP (C, C', C”) or UAS-vam-Δ-SH3-3-RFP (D, D', D”) showing how the different SH3 domains of Vam (red) affect its co-localization with Dachs:GFP (D:GFP) (green) in the presence of elgiCS. (E) Schematic illustrating model showing that under normal conditions Elgi maintains limiting levels of Dachs (green circles) which localizes to the membrane in an App-dependent manner. In absence of App, Dachs is mostly found in the cytoplasm in a diffuse manner and in absence of Elgi there is higher amount of Dachs, but the endogenous App is sufficient to promote its membrane localization. However, in absence of both, there is excessive Dachs that fails to localize to the membrane and accumulates in punctae in the cytoplasm. Elgi might regulate lysosomal trafficking of a Dachs/Vam complex, or direct proteosomal degradation of a Dachs/Vam complex. EE: early endosome, MVB: multi vesicular body, CRE: common recycling endosome, RE: recycling endosome, LE: late endosome. Scale bar is 16.5 μm in A-D.