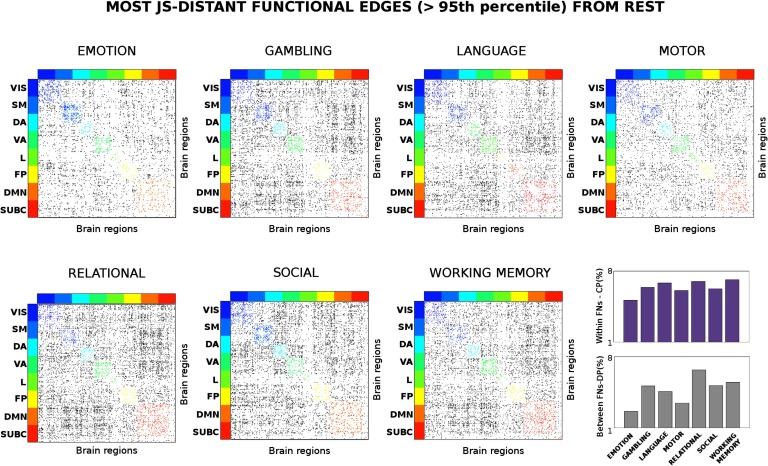
Figure 2. .
Connectivity distance across different tasks. Evaluation of the most distant functional links (in terms of Jensen-Shannon [JS] distance; see Methods) across seven different task sessions. The JS matrices were thresholded at the 95th percentile of the distribution of JS values across the seven tasks. The JS matrices were then ordered by seven functional networks (FNs; Yeo et al., 2011); visual (VIS), somatomotor (SM), dorsal attention (DA), ventral attention (VA), limbic (L), frontoparietal (FP), and default mode network (DMN). An eight subcortical network (SUBC) was added for completeness. The edges surviving the threshold corresponding to within-FN connections are color-coded accordingly. Edges corresponding to between-FN connections are depicted in gray scale. Note how the connectivity distance depends on the task: in some cases within-FN connectivity is more recruited (i.e., for the emotion task), in other between-FN connections are the most distant (i.e., relational task). The bottom-right bar plots depict the average percentage of within-FN most distant edges, i.e., centralized processing (CP, violet bars) and the average percentage of between-FN edges, that is, distributed processing (DP, gray bars) across the different tasks.