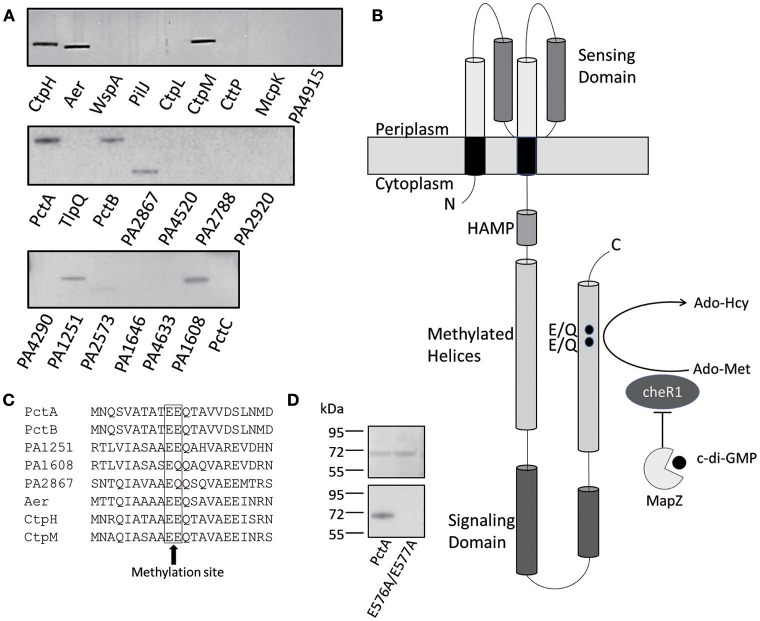
Figure 1.
CheR1-catalyzed methylation of eight MCPs. (A) Methylation of eight MCPs by CheR1 demonstrated by in vitro methyltransferase assay with the methylated MCPs visualized by radioautography. The membrane fraction-containing chemoreceptor and [3H] Ado-Met were used as the substrate and co-substrates for CheR1, respectively. The amount of membrane fraction was normalized according to the corresponding protein expression level. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (B) Schematic representation of the architecture of PctA with the ligand-binding domain located in the periplasm and the cytoplasmic portion comprised of a HAMP domain, methylated helices and a signaling domain. The MapZ-mediated inhibition of CheR1 by c-di-GMP is depicted along with the predicted methylation sites (E/Q) in the methylated helices. (C) Partial sequence alignment of the eight MCP substrates of CheR1 with the predicted methylation sites are shown in the frame. (D) In vitro methyltransferase assay shows the methylation of PctA, but not PctAE576AE577A, by CheR1. The membrane fraction-containing MCP and [3H] Ado-Met were incubated with CheR1 before the methylated MCP was visualized by radioautography. SDS-PAGE gel (upper panel) shows that the amount of MCP proteins used in the assay were comparable. The methylated MCPs were visualized by radioautography (lower panel). Data are representative of two independent experiments.