Fig. 2.
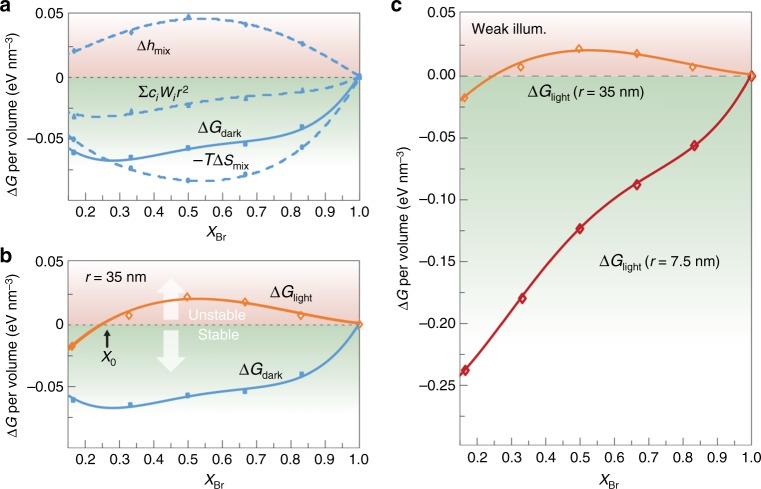
A thermodynamic nucleation model explains the dependence of phase stability on the morphology. a The calculated ΔGdark per volume (solid line) is negative regardless of the Br content. The dashed lines show the calculated volumetric enthalpy Δhmix, volumetric entropy term TΔsmix, and cohesive energy ΣciWir2. A relatively large grain size was used here (r = 35 nm). b Under illumination, the calculated free energy ΔGlight becomes partially positive assuming the same grain size. A threshold composition X0~0.3 divides the mixed-halide perovskites into stable (I-rich) and unstable (Br-rich) regions. c To mimic the experimental conditions of the CsPb(BrxI1-x)3/Cs4Pb(BrxI1-x)6 composites, a small grain size (r = 7.5 nm) was assumed and the cohesive energy was considered. The calculated ΔGlight turns negative, indicating a stable phase of homogenous mixed-halide perovskites