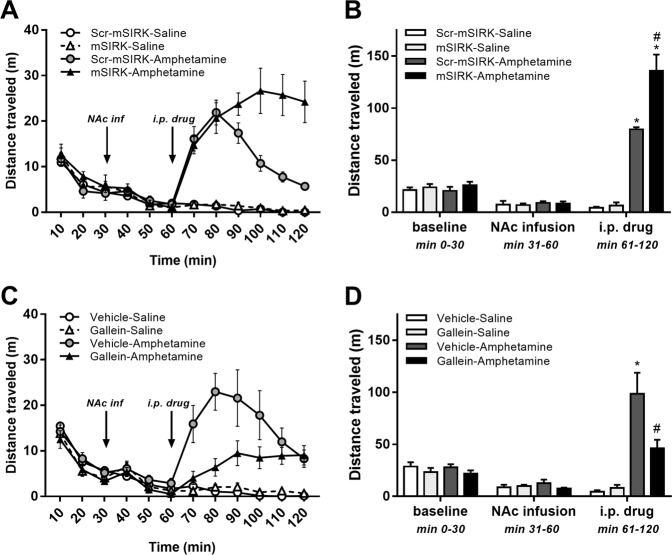
Fig. 1. Activation of Gβγ subunits in the nucleus accumbens prolongs and inhibition of Gβγ subunits in the nucleus accumbens blunts amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion.
a Means ± s.e.m. of distance traveled across the 2 h testing period, depicted per 10 min block, for the scr-mSIRK-saline (n = 6), mSIRK-saline (n = 6), scr-mSIRK-amphetamine (n = 6) and mSIRK-amphetamine (n = 6) groups. Scr-mSIRK or mSIRK was infused into the nucleus accumbens (NAc) 30 min before saline or amphetamine injection. b Means ± s.e.m. of distance traveled by experimental period for the same groups. NAc infusion is the period immediately after intra-NAc infusion of scr-mSIRK, and intraperitoneal (i.p.) drug is the period immediately after saline or amphetamine injection. Habituation was performed in drug-free conditions. c Means ± s.e.m. of distance traveled across the 2 h testing period, depicted per 10 min block, for the vehicle-saline (n = 6), gallein-saline (n = 6), vehicle-amphetamine (n = 6) and gallein-amphetamine (n = 6) groups. Vehicle or gallein was infused into the NAc 30 min before saline or amphetamine injection. d Means ± s.e.m. of distance traveled by experimental period for the same groups. NAc infusion is the period immediately after intra-NAc infusion of vehicle of gallein, and i.p. drug is the period immediately after saline or amphetamine injection. Habituation was performed in drug-free conditions. *P < 0.05 between saline-treated and amphetamine-treated groups; #p < 0.05 between scr-mSIRK-amphetamine and mSIRK-amphetamine groups b or between vehicle-amphetamine and gallein-amphetamine groups d