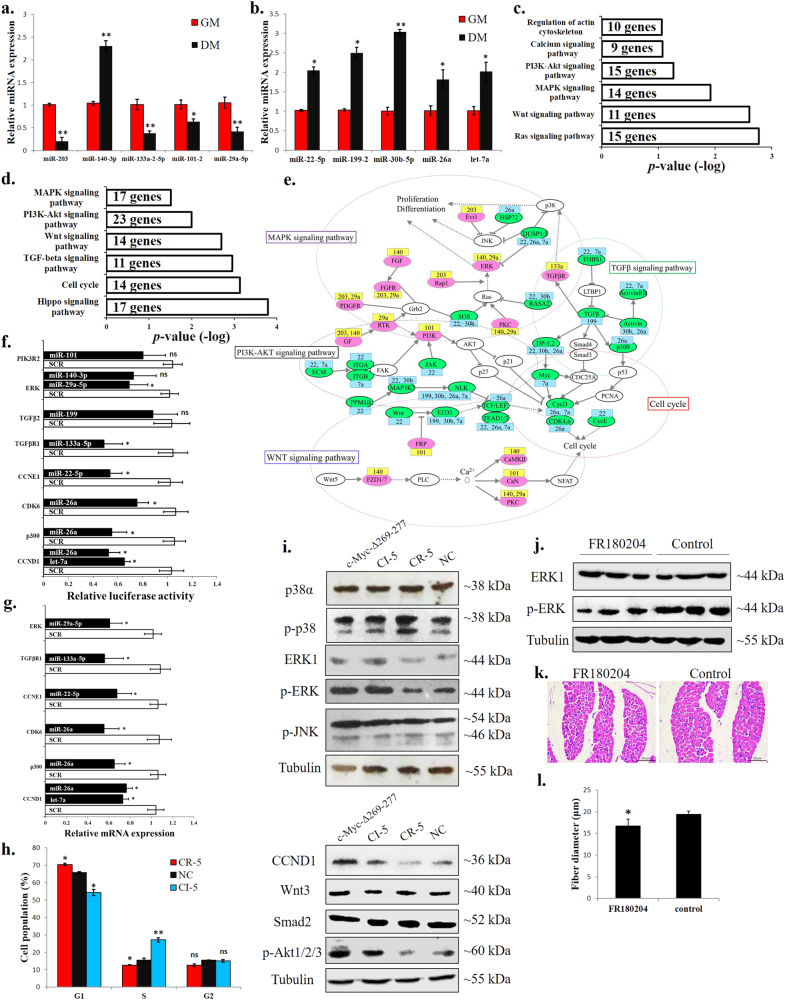
Fig. 6.
c-Myc-associated miRNAs are involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, ERK–MAPK and Akt-mediated pathways. a Relative miRNA expression of the CI-5s between GM and DM. b Relative miRNA expression of the CR-5s between GM and DM. c KEGG analysis of the CI-5 target genes. d KEGG analysis of the CR-5 target genes. e Gene-miRNA network consisting of 57 proteins (from the CI-5 and CR-5 target genes enriched in the indicated pathways) and their connections (grey lines). miRNA targets are displayed in green and pink. Targets in pink indicate genes upregulated from GM to DM. Targets in green indicate genes downregulated from GM to DM. miRNA names are reported in the yellow and blue boxes. CI-5s are shown in yellow, and CR-5s are shown in blue. The dotted line marks the areas with nodes belonging to canonical pathways. f Relative luciferase activity of 3’ UTR reporter constructs in certain genes shown in figure (e) after transfection with selected miRNA mimics. g Relative mRNA expression after transfection of individual CR-5 miRNAs in chicken primary myoblast. h Primary myoblasts expressing CR-5s, CI-5s or NC were cultured in GM, and the cell cycle phase was analysed after 2 days. i Primary myoblasts were transfected with c-Myc-Δ269–277, CI-5s, CR-5s or NC, and the protein levels of the indicated proteins were analysed after 3 d. j Chicken breast muscles were injected with FR180204 or control, and the protein levels of the ERK1 and p-ERK were analysed. k H–E staining of breast muscle fibre cross sections from chickens injected with FR180204 or control. l Fibre diameter of chicken breast muscles injected with FR180204 or control. The results are shown as the mean ± sem of three independent experiments. In (f (ERK and CCND1), g (CCND1) and h), ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test was used. In (a,b,h,l), independent sample t-test was performed to determine the significant differences between the groups. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ns, no significant difference