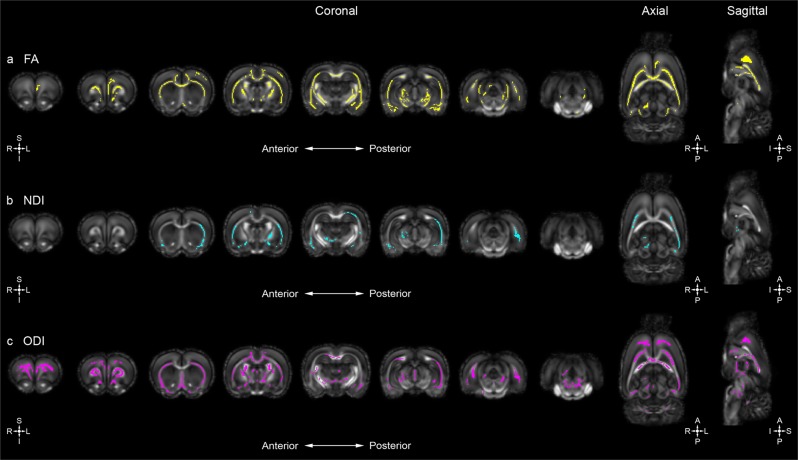
Fig. 2. Disc1 svΔ2 in male rats underlies deficits in white matter microstructural integrity and contributes to global alterations in neurite density and orientation.
a Whole-brain voxel-wise tract-based spatial reveal significant areas of decreased FA in male Disc1 svΔ2 rats (n = 6) compared to matched controls (n = 7) (voxels in yellow). Eight representative coronal sections (left [anterior] to right [posterior]) and single representative axial and sagittal sections reveal significant overlapping regions of decreased FA mainly in the left superior neocortex, external capsule, corpus callosum, internal capsule, and left amygdala. b Disc1 svΔ2 male rats demonstrated significant areas of decreased NDI compared to matched controls (voxels in cyan). Eight representative coronal sections (left [anterior] to right [posterior]) and single representative axial and sagittal sections reveal significant regions of decreased NDI predominantly in the left cerebral hemisphere in the inferior neocortex, external capsule, and right amygdala. c Disc1 svΔ2 male rats demonstrated significant areas of decreased ODI compared to matched controls (voxels in pink). Eight representative coronal sections (left [anterior] to right [posterior]) and single representative axial and sagittal sections reveal significant regions of decreased ODI in the left cerebral hemisphere, and also in a similar spatial distribution in the right hemisphere with decreased ODI spread over a large portion of the superior neocortex, external capsule, and corpus callosum. Some regions of the internal capsule, left amygdala, and left hippocampus also show decreased ODI indices