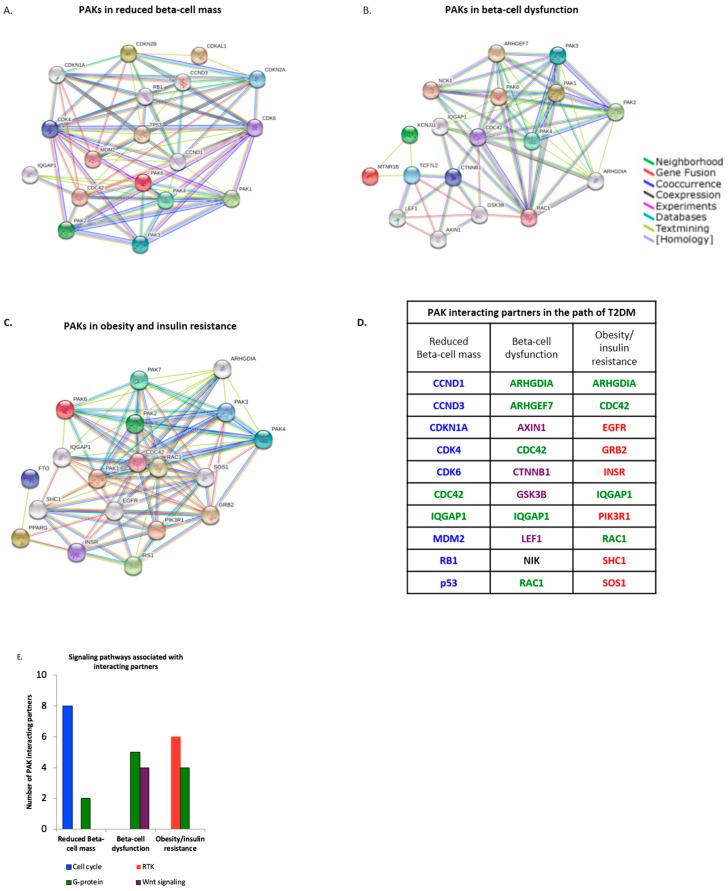
Figure 1.
(A–E) PAK interacting partners are associated with pathogenesis of T2DM. PAK interacting partners were identified with STRING database, using known targets involved in (A) reduced beta-cell mass, (B) beta-cell dysfunction, and (C) obesity/insulin resistance. (D) Novel PAK interacting partners involved in reduced beta-cell mass, beta cell dysfunction, and obesity/insulin resistance are displayed and color coded based on their involvement in the cell cycle (blue); G-proteins (green); receptor tyrosine kinase (red); and Wnt signaling (purple). (E) Bar graphs indicate the number of interacting partners involved in pathway associated with pathogenesis of T2DM. Reduced beta cell mass is associated with the cell cycle, beta cell dysfunction is associated with Wnt signaling, and obesity/insulin resistance is associated with receptor tyrosine kinases. G-proteins are associated with all three pathways leading to T2DM.