Fig. 3.
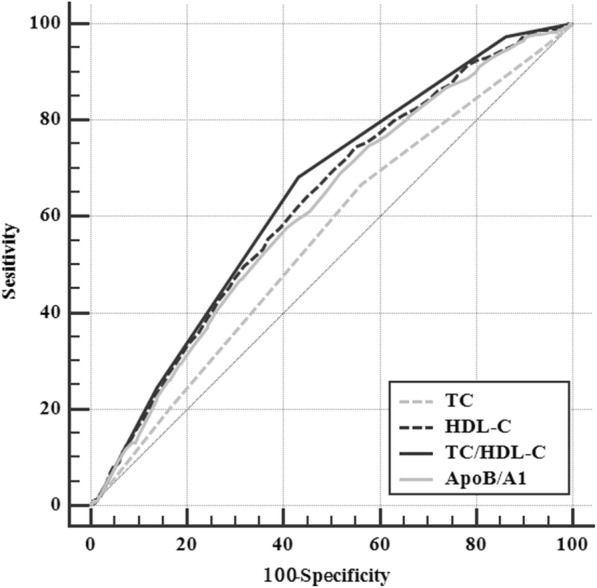
The ROC of TC, HDL-C, TC/HDL-C and ApoB/ApoA1 for NAFLD. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) shows the ability of lipid parameters, including TC, HDL-C (we used the inverse HDL-C instead of HDL-C, because HDL-C had a negative relationship with the risk of NAFLD). TC/HDL-C and ApoB/ApoA1 for the incident of NAFLD. The AUC of TC/HDL-C (0.645 [95%Cl 0.636–0.653]) was greater than that of TC (0.554 [95%Cl 0.545–0.563], P<0.0001), that of HDL-C (0.627 [95%Cl 0.618–0.635], P = 0.0292) and that of ApoB/ApoA1 (0.613 [95%Cl 0.605–0.622], P = 0.0003). TC, Total cholesterol; HDL-C, High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TC/HDL-C, Total cholesterol/ High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; ApoB/ApoA1, Apolipoprotein B/ Apolipoprotein A1
