Fig. 1.
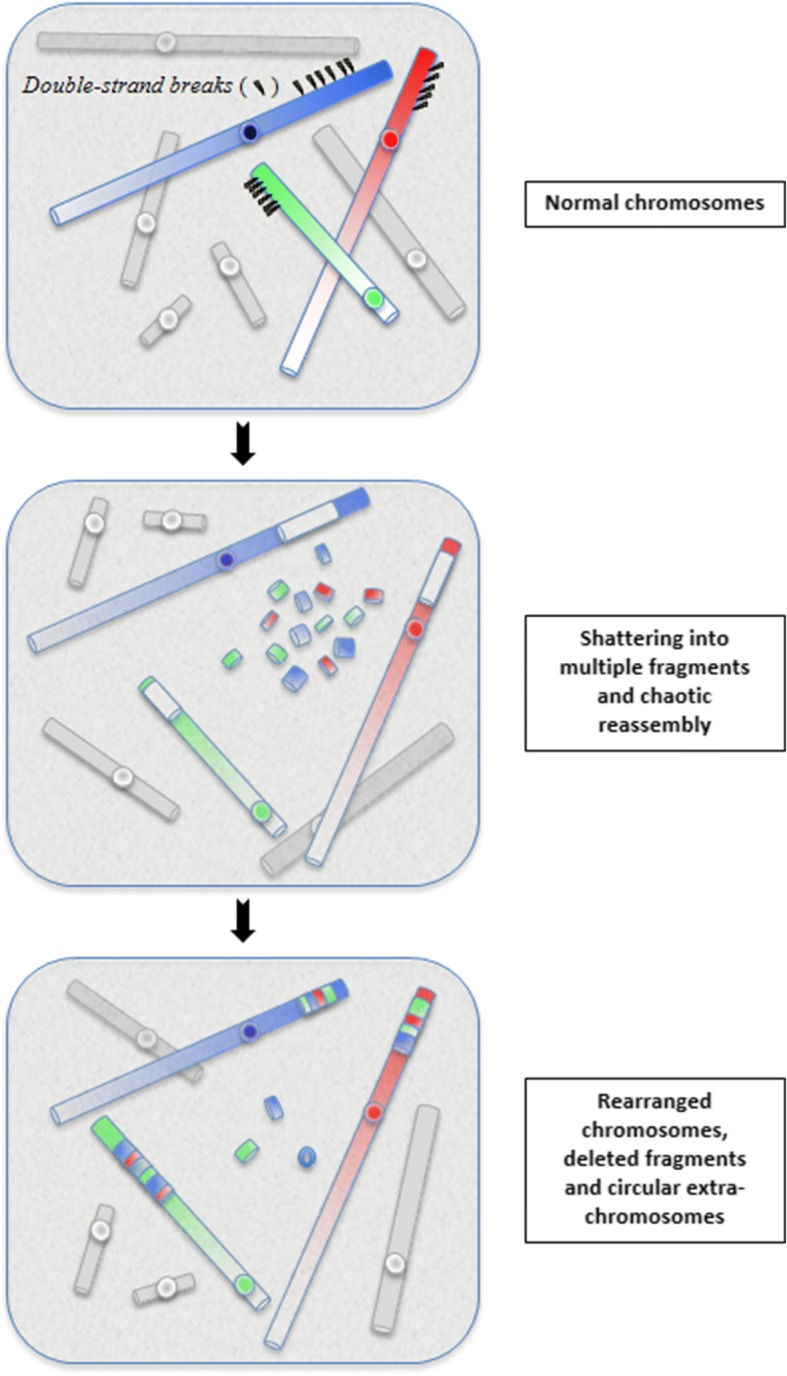
The concept of chromothripsis: during a one-step catastrophic event, multiple double-strand breaks occurred, restricted to a simple chromosomal segment or to a few closed chromosome domains, leading to the pulverization of chromosomal fragments. This shattering can produce tens to hundreds DNA fragments. Most of them are stitched back together by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ), resulting in chaotic derivative chromosome(s), whereas some are lost or combined in small circular extra-chromosomes
