Fig. 5. The effects of 30 mg/kg MTEP and CDPPB upon the behavior of adult mice in the FST.
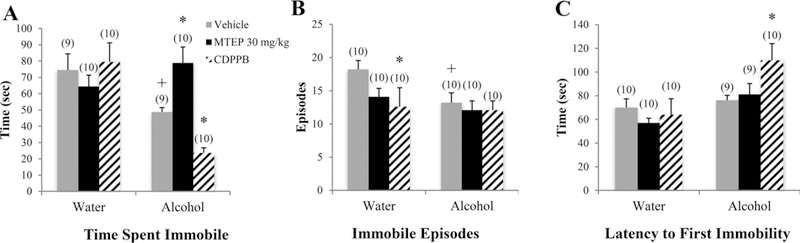
(A) There was a significant drinking X treatment interaction in the time spent immobile. In vehicle-treated animals, alcohol drinkers spent less time immobile compared to water drinkers. In alcohol drinkers, MTEP-treated animals spent more time immobile compared to vehicle treatment while CDPPB-treated animals spent less. (B) In vehicle-treated animals, alcohol drinkers had fewer immobile episodes compared to water drinkers. In water drinkers, CDPPB treatment reduced immobile episodes compared to vehicle treatment. There was also a trend toward reduced immobile episodes in MTEP-treated water drinkers. (C) Alcohol drinkers had a longer latency to first immobility compared to water drinkers; however, this difference was driven primarily by a significant increase in CDPPB-treated alcohol drinkers compared to vehicle treatment. *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle treatment within same drinking group, +p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated water drinkers. Data represent mean + SEM of the number of animals indicated in parentheses.
