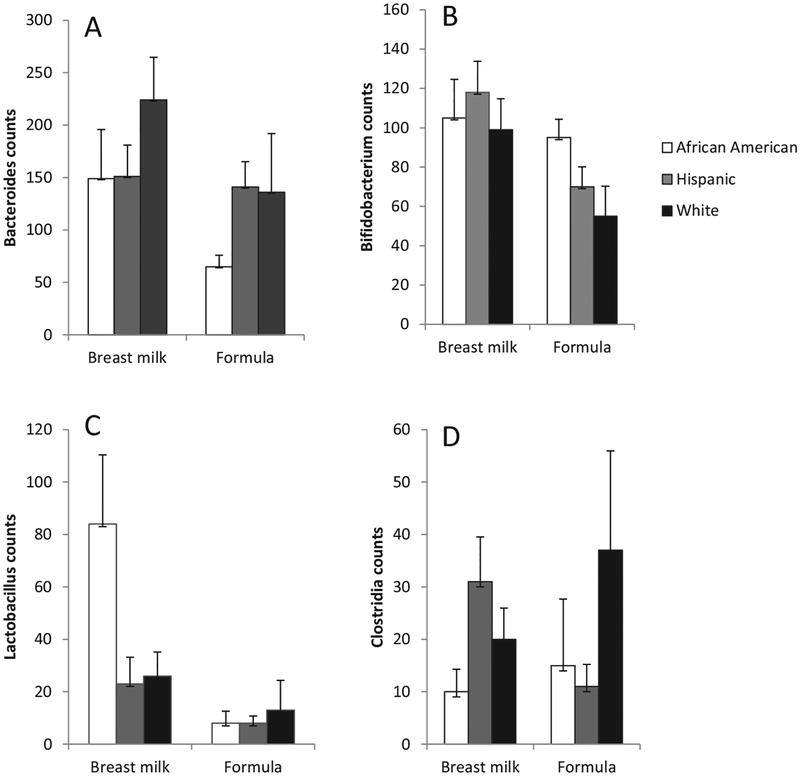
Figure 2.
Average (±SE) counts per 1000 reads of A, Bacteroides, B, Bifidobacterium, C, Lactobacillus, and D, Clostridia spp among infants fed breast milk or formula, stratified by race/ethnicity. There were interactions between race/ethnicity and breastfeeding vs formula on relative abundances of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus (P ≤ .10) in negative binomial regression analyses.