FIGURE 4.
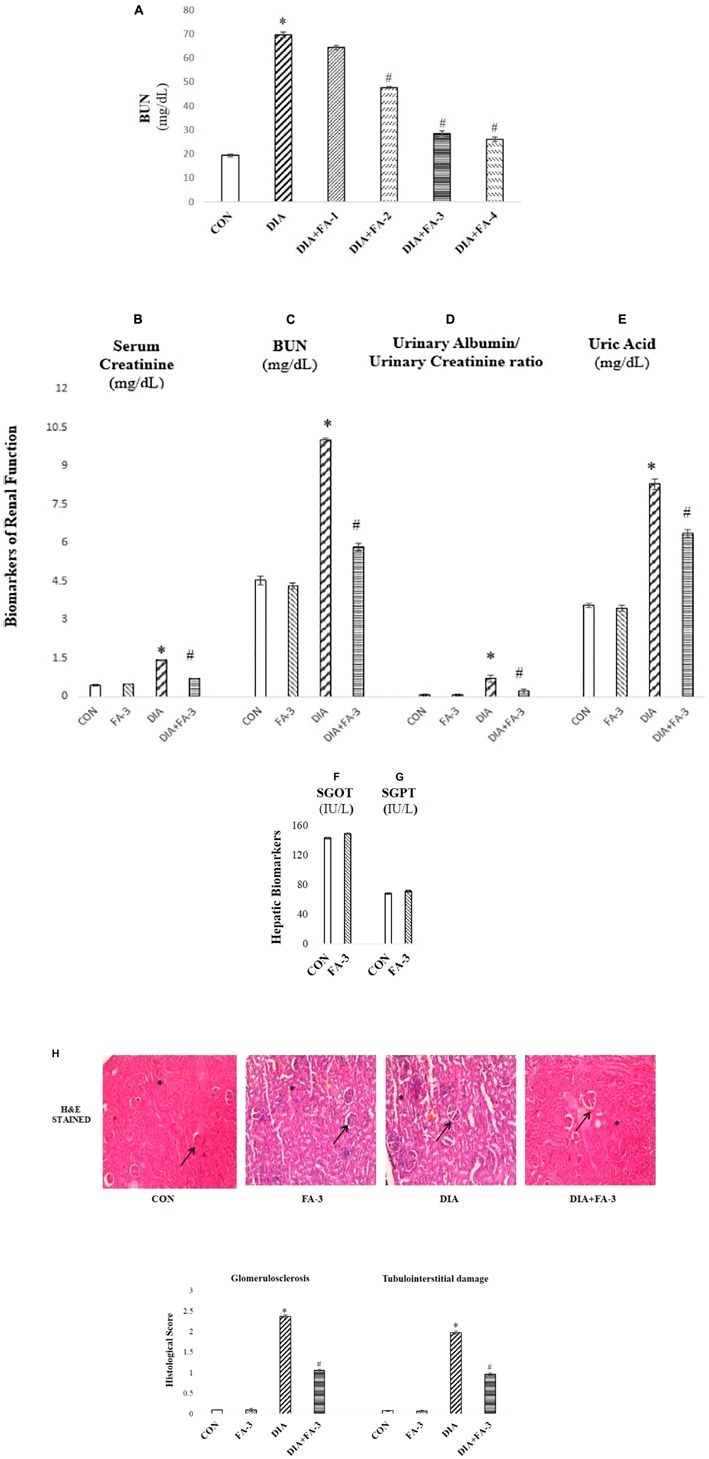
The role of ferulic acid on STZ-mediated nephrotoxicity in type 1 diabetic rats. (A) Effect of ferulic acid on the level of BUN in serum alongside STZ mediated toxicity in the renal tissue of the experimental rats in a dose-dependent manner. CON: BUN level in rats treated with vehicle only; STZ: BUN level in STZ induced diabetic rats; STZ+FA-10, STZ+FA-30, STZ+FA-50, STZ+FA-70: BUN level in ferulic acid treated diabetic rats for 8 weeks at varied doses viz. 10, 30, 50, and 70 mg kg-1 body wt. respectively; (B) serum creatinine level; (C) BUN level; (D) urinary albumin/urinary creatinine ratio; (E) level of uric acid; (F) SGOT level; (G) SGPT level; (H) Histological examination. H&E staining of sections of kidney tissues of rats; ×200 and histological score. CON: rats receiving vehicle only; FA-3: only ferulic acid treated rats (dose: 50 mg kg-1 body wt.); STZ: receiving STZ (50 mg kg-1 body wt.); STZ+ FA-3: post-diabetic induction, rats treated with ferulic acid (dose: 50 mg kg-1 body wt.). Values are represented as mean ± SEM (six animals in each experimental groups) for three different experiments. “∗” symbolizes values differing from CON (∗P < 0.05) significantly; “#” denotes values differing from DIA (#P < 0.05) significantly; no significant variance existed between untreated (CON) and ferulic acid treated (FA-3) groups.
