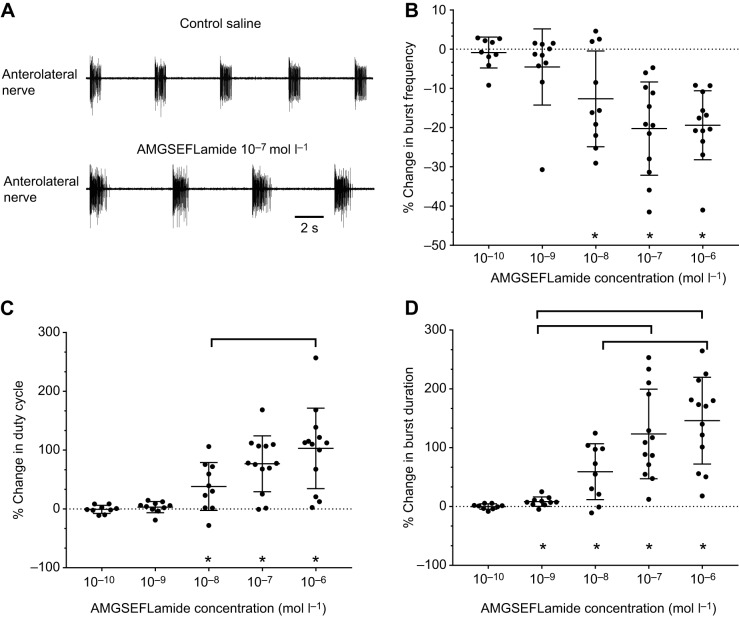
Fig. 5.
AMGSEFLamide modulates CG output. (A) Recordings of activity in the anterolateral nerve in control saline and during bath application of 10−7 mol l–1 AMGSEFLamide. AMGSEFLamide elicited an increase in burst duration and a decrease in cycle frequency. (B–D) Graphs depicting changes in CG cycle frequency (B), duty cycle of motor neuron bursts (C) and duration of motor neuron bursts (D) in response to bath application of AMGSEFLamide at concentrations ranging from 10−10 to 10−6 mol l–1. (B) Threshold concentration for changes in cycle frequency was ∼10−8 mol l–1; at concentrations of 10−8 mol l–1 and higher, the percent change in burst frequency decreased significantly (Wilcoxon signed rank test against a theoretical median of 0, two-tailed: 10−10 mol l–1, P=0.9102; 10−9 mol l–1, P=0.1309; 10−8 mol l–1, P=0.0273; 10−7 mol l–1, P=0.0005; 10−6 mol l–1, P=0.0005). However, changes in cycle frequency were not concentration dependent; all concentrations above threshold elicited similar effects (ANOVA, P=0.2345). (C) Threshold concentration for changes in duty cycle was ∼10−8 mol l–1, with 10−8 mol l–1 and higher concentrations eliciting significant changes in duty cycle (Wilcoxon signed rank test; theoretical median of 0, two-tailed: 10−10 mol l–1, P=0.7344; 10−9 mol l–1, P=0.1934; 10−8 mol l–1, P=0.0137; 10−7 mol l–1, P=0.0005; 10−6 mol l–1, P=0.0002). The response to AMGSEFLamide increased with increasing concentrations (ANOVA, P=0.0279), with a significant difference between responses to 10−8 and 10−6 mol l–1 (Tukey's multiple-comparison test, P=0.0211). (D) Threshold for changes in burst duration elicited by AMGSEFLamide was ∼10−9 mol l–1; concentrations of 10−9 mol l–1 and higher elicited significant changes in burst duration (Wilcoxon signed rank test; theoretical median of 0, two-tailed: 10−10 mol l–1, P=0.9102; 10−9 mol l–1, P=0.0098; 10−8 mol l–1, P=0.0098; 10−7 mol l–1, P=0.0002; 10−6 mol l–1, P=0.0002). Changes in burst duration were concentration dependent (ANOVA, P<0.0001), with burst duration increasing as peptide concentration increased. Responses to 10−9 mol l–1 AMGSEFLamide differed significantly from those to 10−7 and 10−6 mol l–1 peptide; responses to 10−8 mol l–1 also differed from those to 10−6 mol l–1 peptide (Tukey's multiple-comparison test; 10−9 mol l–1 versus 10−7 mol l–1, P=0.0003; 10−9 mol l–1 versus 10−6 mol l–1, P<0.0001; 10−8 mol l–1 versus 10−6 mol l–1, P=0.0080). An asterisk (*) indicates averages significantly different from zero. Square brackets indicate significant differences between responses to peptide concentrations. For all parameters (B–D): 10−10 mol l–1, n=9; 10−9 mol l–1, n=10; 10−8 mol l–1, n=10; 10−7 mol l–1, n=13; 10−6 mol l–1, n=13.