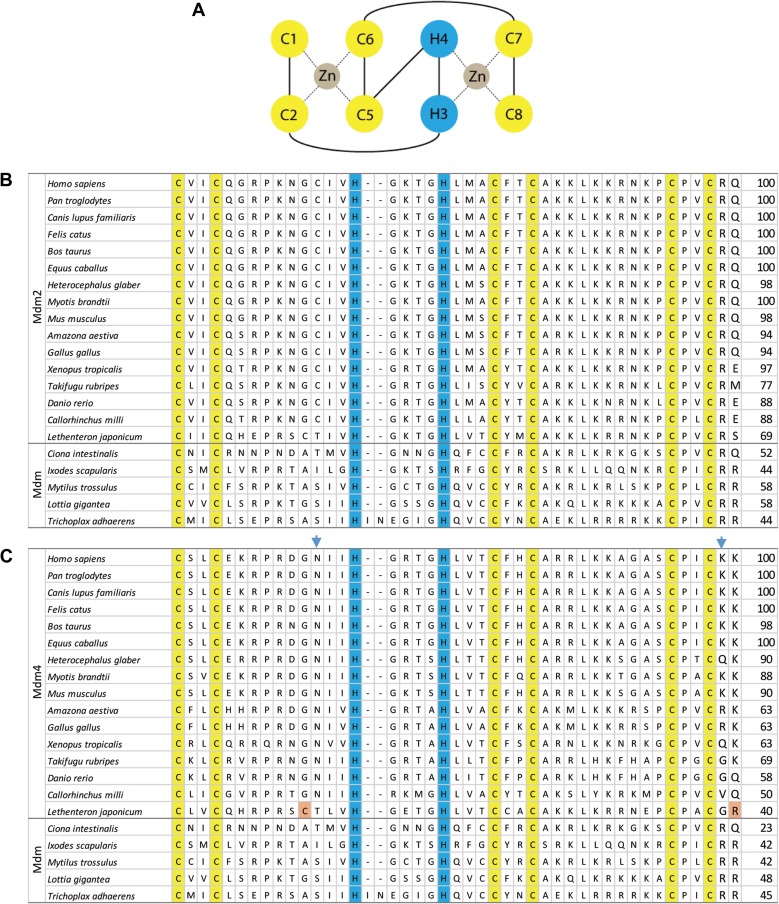
Figure 1.
The RING finger domains of Mdm2 and Mdm4. (A) The Mdm2/Mdm4 RING finger motif consists of an octet of two cysteines (C1 and C2), two histidines (H3 and H4) and four cysteines (C5–C8). Two zinc ions are bound in coordinate bonds (dotted lines) by half of the motif (C1+C2+C5+C6 and H3+H4+C7+C8). (B) This C2H2C4 cross-brace motif is conserved in vertebrate Mdm2 and invertebrate Mdm. The cysteine and histidine residues involved are numbered and highlighted in yellow and blue, respectively. (C) The blue arrowheads indicate the asparagines (N448 in humans) that can be substituted to cysteines, as well as lysines (K478 in humans) to arginines, to make the Mdm4 functional E3 ligases. The residues highlighted in orange present in L. japonicum Mdm4 potentially make them functional E3 ligases. The numbers on the right of the table indicate the percentage identity compared to H. sapiens Mdm2 or Mdm4.