Figure 2. Δg NK Cells Are Primed by CMV Status.
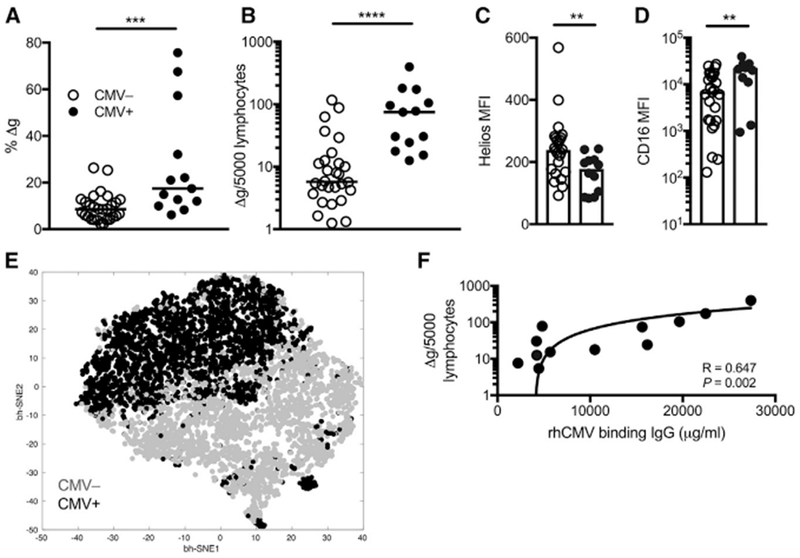
(A–D) Frequencies among bulk NK cells (A) and normalized circulating numbers of Δg NK cells (B) are shown for rhCMV-uninfected (n = 28) and rhCMV-infected (n = 14) rhesus macaques. Horizontal lines indicate medians. Density of intracellular Helios (MFI, median fluorescence intensity) (C) and surface CD16 on Δg NK cells (D) in peripheral blood nuclear cells (PBMCs) from rhCMV-uninfected and rhCMV-infected macaques. Bars indicate medians.
(E) Composite phenotypic t-SNE plot of Δg NK cells only down-selected in both rhCMV-uninfected and rhCMV-infected rhesus macaque cohorts showing near complete independent multidimensional clustering by rhCMV-specific IgG levels; data points represent individual cells.
(F) Correlation of circulating Δg NK cell numbers with rhCMV-binding antibody equivalents.
Statistical evaluations were made with Mann Whitney U or Spearman’s correlation test; **p <0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
