Fig. 2.
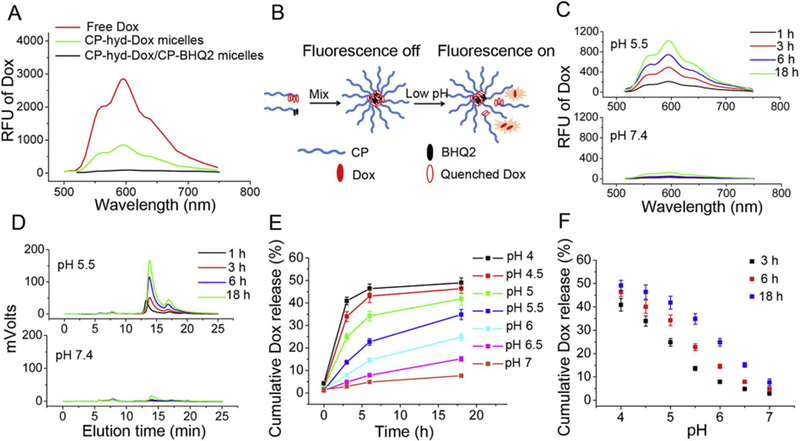
Acid triggers Dox release from pH-sensitive CP-hyd-Dox/CP-BHQ2 mixed micelles (hyd: hydrazone linker) in sodium phosphate buffer studied by Dox fluorescence de-quenching. (A) The Dox fluorescence emission spectra of ~5.3 μM (Dox concentration) free Dox, CP-hyd-Dox micelles and CP-hyd-Dox/CP-BHQ2 mixed micelles excited at 470 nm. Dox fluorescence is partly quenched in CP-hyd-Dox micelles and completely quenched in CP-hyd-Dox/CP-BHQ2 mixed micelles. (B) Scheme of measuring Dox release from micelles by fluorescence de-quenching. CP-hyd-Dox/CP-BHQ2 self-assembles into micelles in aqueous solution and Dox is completely quenched by BHQ2 in the micelle core. When Dox is released from the micelles upon acid-triggered cleavage of hydrazone linkers, Dox separates from BHQ2 and recovers its red fluorescence. (C) Dox release studied by fluorescence spectroscopy. CP-hyd-Dox/CPBHQ2 mixed micelles were incubated in aqueous solution at pH 5.5 or pH 7.4. (D) Dox release studied by SE-HPLC. CP-hyd-Dox/CP-BHQ2 was separated from released free Dox and Dox fluorescence was measured. The retention times of CP-hyd-Dox/CP-BHQ2 and released Dox start at ~5.5 min and ~13.7 min, respectively. (E, F) Time- and pH-dependent Dox release from CP-hyd-Dox/CP-BHQ2 mixed micelles measured by fluorescence spectroscopy.
