Fig. 3.
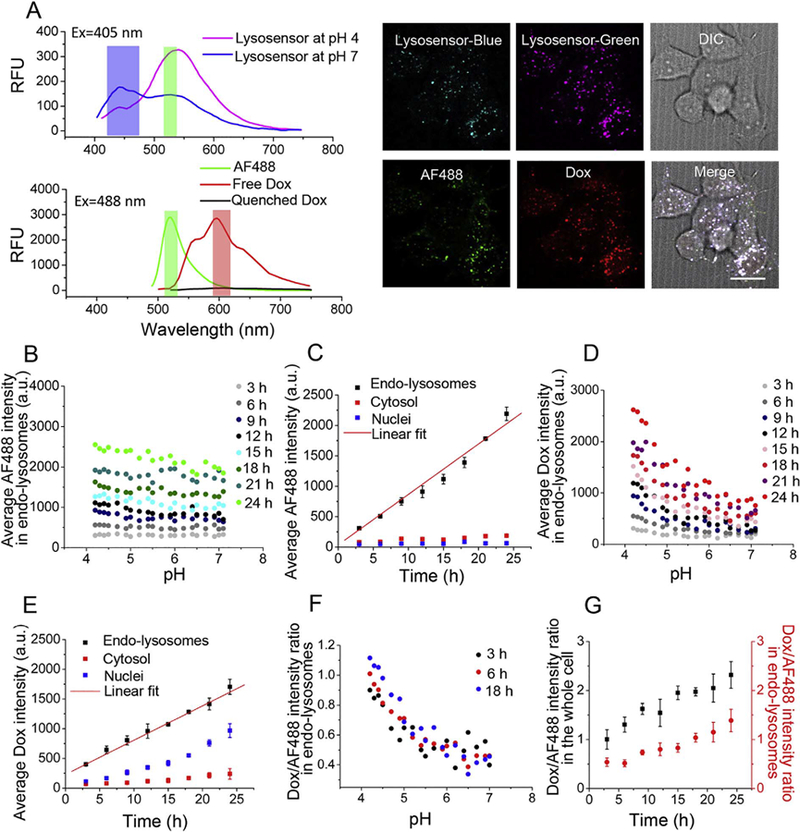
Acid triggers Dox release from pH-sensitive AF488-labeled CP-hyd-Dox/CP-BHQ2 mixed micelles (hyd: hydrazone linker) in endo-lysosomes. (A) The top panel shows the fluorescence emission spectrum of Lysosensor at pH 4 and pH 7 excited at 405 nm, and the bottom panel shows the fluorescence emission spectra of AF488, free Dox and quenched Dox excited at 488 nm. The blue, green and red bars indicate the emission filters used for fluorescence emission measurements. Live cells were incubated with AF488-labeled CP-hyd-Dox/CPBHQ2 mixed micelles and Lysosensor, and then were imaged by a spinning disk confocal microscope. The panel on the right shows representative blue and green fluorescence images of Lysosensor, a green fluorescence image of AF488, a red fluorescence image of Dox and a DIC image of cells. The white scale bar indicates 2 μm. (B) Average AF488 intensity in endolysosomes as a function of pH over time. Endo-lysosomal distribution of AF488-labeled CP is invariant across all pH but increases with time. (C) Average AF488 intensity in endo-lysosomes, cytosol and nuclei over time. AF488-labeled CP accumulates in endo-lysosomes with linear kinetics and does not traffic to the cytosol and nuclei. (D) Average Dox intensity in endo-lysosomes against pH over time. Dox fluorescence, which derives from the released drug, shows preferred accumulation in the low pH environment of endo-lysosomes after 6 h. (E) Average Dox intensity in endo-lysosomes, cytosol and nuclei over time. Released Dox accumulates in endo-lysosomes with linear kinetics, and it diffuses to the cytosol and accumulates in the nuclei over time, with minimal accumulation in the cytosol. (F) Dox/AF488 intensity ratio in endo-lysosomes as a function of pH at different time points changes inversely with pH below pH 6. (G) Dox/AF488 intensity ratio in endo-lysosomes and in the whole cell increases over time.
