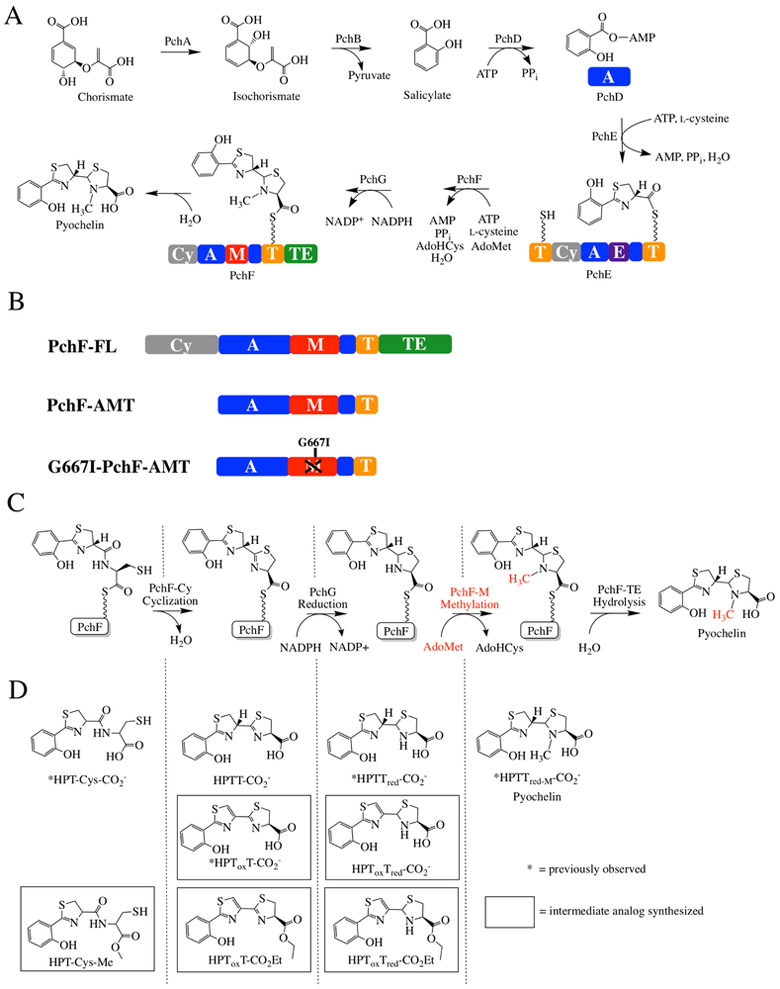
Figure 1: Synthesis of pyochelin.
A) Biosynthetic pathway for pyochelin production. PchA, an isochorismate synthase, and PchB, an isochorismate pyruvate lyase, convert chorismate to salicylate. PchD-G consists of 12 different domains constituting three NRPS modules with three tailoring domains. Together, they assemble pyochelin from salicylate and two l-cysteines, with co-substrates AdoMet, ATP, and NADPH. AdoMet = S-adenosylmethionine, AdoHcys = S-adenosylhomocysteine. PchD is a stand-alone adenylation domain (A; blue). PchE has N- and C-terminal thiolation domains (T; yellow), a cyclization domain (Cy; grey), an adenylation domain (A; blue) and a stuffed epimerase domain (E; purple). PchG is a stand-alone NADPH-dependent reductase. PchF is a full-NRPS module consisting of 5 different domains: a cyclization domain (Cy; grey), adenylation domain (A; blue), stuffed methyltransferase tailoring domain (M; red), thiolation domain (T; yellow), and thioesterase domain (TE; green). B) PchF-FL refers to the “full-length” protein, whereas PchF-AMT only includes the stuffed adenylation methyltransferase didomain and the thiolation domain. G667I-PchF-AMT has a mutation to the proposed AdoMet binding domain of the variant PchF-AMT. C) The proposed order of chemistries performed by PchF. PchF incorporates l-cysteine to the growing peptide chain. The Cy-domain of PchF continues chain elongation by generating a peptide bond between l-cysteine and the upstream hydroxyphenyl-d-thiazoline moiety of PchE (an intermediate attached to the Ppant of the T-domain of PchE). The Cy-domain then cyclizes the cysteine to form a hydroxyphenyl-(d)-thiazoline-(l)-thiazoline intermediate. PchG (green) reduces the terminal thiazoline of the hydroxyphenyl-bis-heterocycle to thiazolidine using NADPH. The stuffed methyltransferase domain of PchF catalyzes the AdoMet-dependent methyl transfer (highlighted in red) onto the nitrogen of the newly reduced thiazolidine ring before transferring the complete heterocyclic siderophore to the TE-domain releasing the fully mature pyochelin by hydrolysis in the TE-domain. The alternate synthetic schemes where methyl transfer occurs at a different position in the sequence of biosynthesis are shown in Figure S1. D) During reconstitution assays, premature hydrolysis releases peptidyl intermediates during biosynthesis. Intermediates previously recovered by Walsh and colleagues are noted with an asterisk. Intermediate analogs used as potential substrates in this study are surrounded by a square. Nomenclature of intermediates is as follows: HP, hydroxyphenyl; Tox, thiazole; T, thiazoline; Tred, thiazolidine; CO2- carboxyl; Et, ethyl; Me/M, methyl.