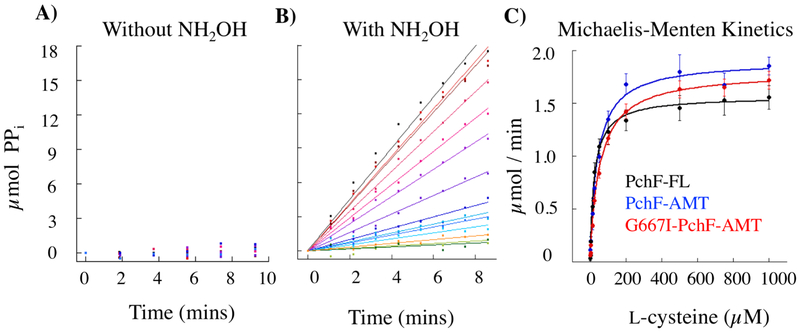
Figure 2: Adenylation activity of PchF variants.
PchF catalyzes the adenylation of l-cysteine by ATP forming an aminoacyl-adenylate bond, releasing pyrophosphate. In the adenylation assay (Figure S3), pyrophosphate is converted to two inorganic phosphates by inorganic pyrophosphatase. 7-methylguanosine is then phosphorylated by purine nucleoside phosphorylase to generate 7-methylguanine, which absorbs at 360 nm. A) PchF variants do not turnover with l-cysteine and ATP (A), but do with the addition of hydroxylamine as a nucleophilic surrogate (B). Michaelis-Menten steady-state kinetics (C) were performed to compare the l-cysteine adenylation activity of PchF-FL, PchF-AMT, and the methyltransferase null mutant of G667I-PchF-AMT.