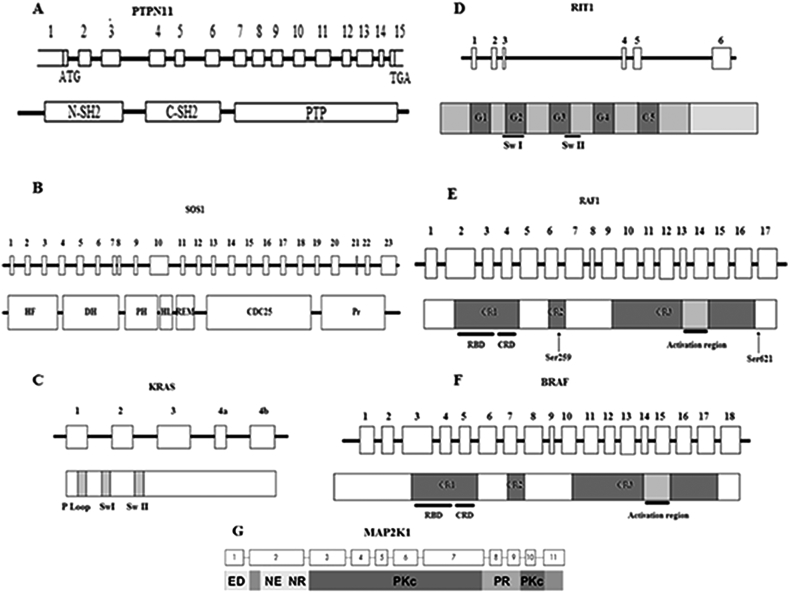
Figure 1.
Organization of Noonan syndrome causing genes and domains, A. PTPN11 exons and SHP-2 domains, B. SOS1 exons and domains, C. KRAS coding exons and domains. In most cases, the exon 4a is spliced out. D. RIT1 coding exons and domains. E. RAF1 coding exons and domains with the localization of Ser259 and Ser621 residues that is critical for RAF1 auto-inhibition. F. BRAF coding exons and domains. G. MAP2K1 coding exons and domains. C-SH2: C-amino-terminal src-homology 2, CR: Conserved Region, CRD: Cysteine-Rich Domain, DH: Dbl Homology, HF: Histone-like Fold, HL: Helical Linker, N-SH2: N- amino-terminal src-homology 2, PH: Pleckstrin Homology, Pr: Proline-riche motif, PTP: protein-tyrosine phosphatase, RBD: RAS binding domain, REM: RAS Exchange Motif, Sw: Switch.