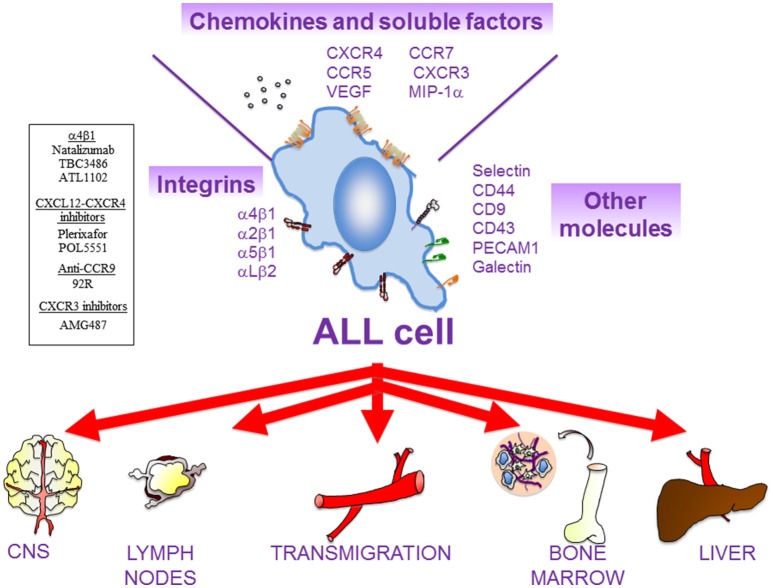
Figure 3.
Main actors of ALL cell migration. There are multiple cell surface receptors and soluble molecules that drive ALL cell movement. ALL cells might remain in the BM or colonize multiple extramedullary organs, such as central nervous system (CNS), lymph nodes (LNs), liver, and testes. In general, β1 integrins (α4β1, α2β1, α5β1) and the integrin αLβ2 are critical for the homing of ALL cells into the BM and for their infiltration in most of the extramedullary organs. The chemokine receptor CXCR4 mediates ALL cell infiltration into BM, liver, lung, and CNS, whilst CCR7 controls ALL infiltration into CNS and LNs. CXCR3 is also critical for CNS infiltration. Other molecules that might contribute to ALL migration includes MIP-1α, VEGF, PECAM-1, VE-Cadherin (for CNS infiltration); IL-7 (for LNs); and CD44 (for BM). Several compounds targeting molecular players in ALL cell migration that are currently being tested in preclinical trials are shown on the left.