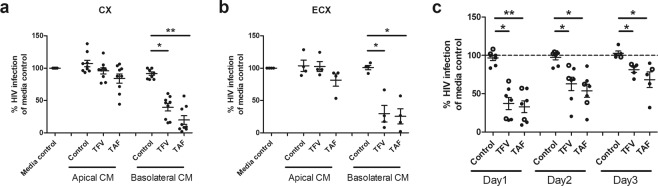
Figure 3.
Secretions from endocervical and ectocervical epithelial cells treated with TFV or TAF inhibit HIV infection of CD4+ T cells. Apical and basolateral conditioned media (CM) were collected from endocervix (CX) and ectocervix (ECX) epithelial cells pre-treated with TFV (3277 µM) or TAF (10 µM) for 24 hr. CM were collected 24 hr post ARV washout and incubation with fresh media; CM was incubated with activated CD4+ T cells prior to HIV infection. Secreted p24 levels in the culture media after 5 days of infection were measured by p24 ELISA as described in Methods. Data are normalized to the infection of CD4+ T cells in the absence of CM (media control) which is set to 100% using (a) CM from CX epithelial cells from 9 patients, (b) CM from ECX epithelial cells from 4 patients. (c) Time course of HIV protection of CD4+ T cells by basolateral CM from CX (dark circles) and ECX (open circles) epithelial cells pre-treated with either ARVs for 24 hr prior to wash out. Cells were then incubated with fresh media that was replaced each day for 3 days, basolateral CM was collected daily. Activated CD4+ T cells were treated for 24 hr with CM. Following washout of CM, CD4+ T cells were infected after which secreted p24 levels measured by p24 ELISA as described in Methods. Data are normalized to the infection of CD4+ T cells in the absence of CM (media control) which is set to 100% (dashed line). (n = 7 individual patients). Columns and horizontal lines represent the mean and SEM respectively. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01.