Fig. 3.
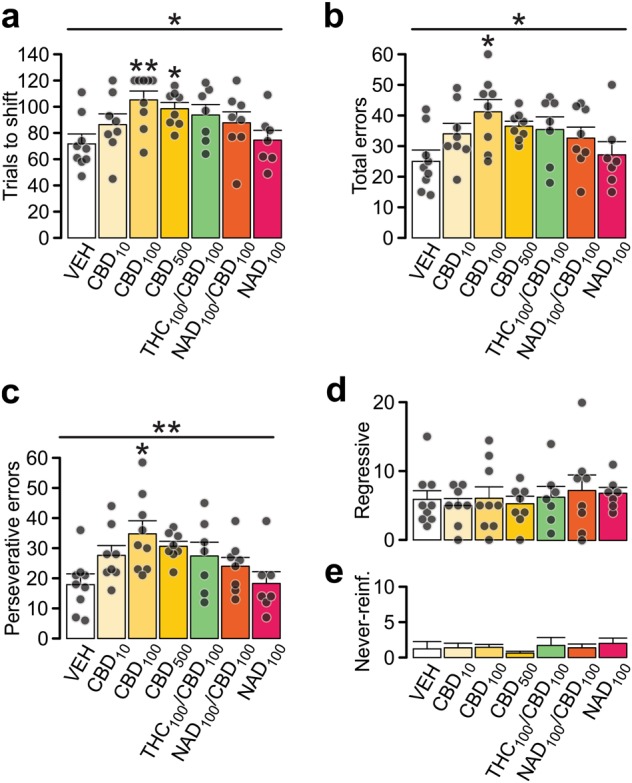
Intra-PFC CBD treatment impairs attentional set-shifting. a The number of trials needed to set-shift from visual to response strategy was increased with intra-PFC CBD treatment. Subscript numbering indicates drug concentrations in ng/hemisphere. Black circles indicate data points (not shown in (e) for clarity). The CBD-induced impairment was weakened by co-application of THC or the 5-HT1a receptor antagonist, NAD299. NAD299 alone did not affect set-shifting. b, Total number of errors performed during set-shifting task was increased in the CBD-treated rats. c–e, Errors were categorized into perseverative (c), regressive (d) or never-reinforced (e). Detailed analysis revealed that rats that needed more trials to complete the task showed a specific increase in perseverance suggesting impaired flexibility. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. Group sizes (n): VEH (9, same as in Fig. 2), CBD10 (8), CBD100(9), CBD500(8), CBD100/THC100 (7), CBD100/NAD299100 (8), NAD299100 (7). Respective treatment groups were compared with one-way ANOVA followed with Gabriel post-hoc; or Kruskal–Wallis test followed with Mann–Whitney U tests. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 vs. VEH group
