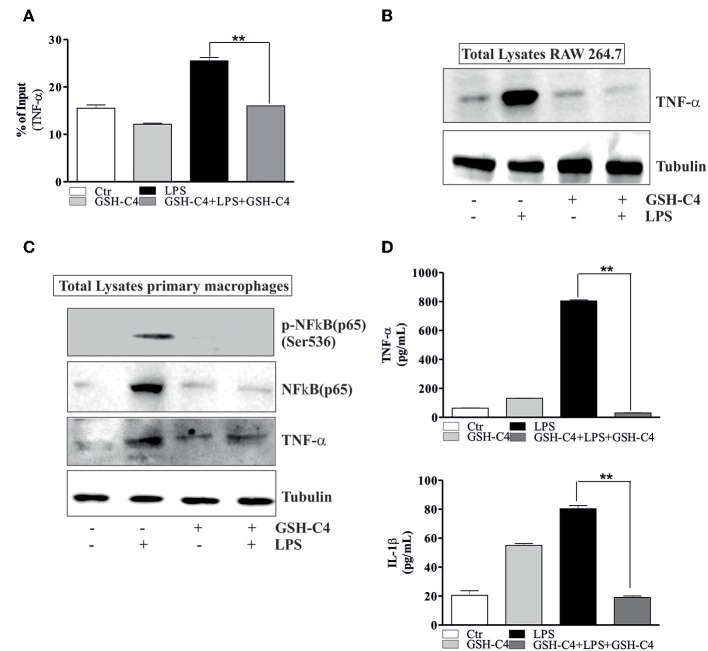
Figure 5.
GSH-C4 treatment prevents the transcription of TNF-α. (A) RAW 264.7 macrophages were treated with 10 mM GSH-C4 for 2 hrs. Subsequently, GSH-C4 was removed from culture medium and the cells were stimulated with 100 ng/ml LPS for 1 hrs. After 1 hrs RAW 264.7 cells were treated again with 10 mM GSH-C4 or fresh medium for 24 hrs. ChIP assay was carried out on crosslinked nuclei using NFκB antibody followed by qPCR analysis of NFκB binding site on TNF-α promoter (+382: ggaggagaTTCCttg). Data are expressed as means ± SD (n = 3; **p < 0.001). (B) Twenty micrograms of total proteins were loaded for Western blot analysis of the TNF-α. Tubulin was used as loading control. (C) 4 × 106 cells/well human macrophages were treated with 10 mM GSH-C4 for 2 hrs. Subsequently, GSH-C4 was removed from culture medium and the cells were stimulated with 100 ng/ml LPS for 1 hrs. After 1 hrs human macrophages were treated again with 10 mM GSH-C4 or fresh medium for 24 hrs. Twenty micrograms of total proteins were loaded for Western blot analysis of the phosphorylated and total form of NFκB [p-NFκB (p65), NFκB (p65)] and TNF-α. Tubulin was used as loading control. (D) TNF-α and IL-1β production in culture supernatants were detected using Elisa Kit (ENZO LifeScience). Data are expressed as means ± S.D. (n = 3; **p < 0.001). All the immunoblots reported are from one experiment representative of three that gave similar results.