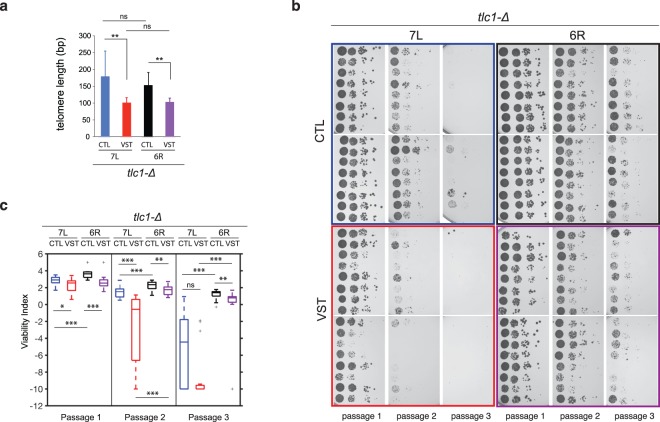
Figure 2.
Effect of the subtelomeric region on replicative senescence. 16 telomerase-negative individual spores carrying the telomere 7L-CTL (blue), 7L-VST (red), 6R-CTL (black) or 6R-VST (purple) (see Fig. 1b,c, e,f) were germinated for two days on selective media. Colonies grown on selective plates for 2 days were then resuspended to equal concentrations and 10-fold dilutions were spotted on solid media, grown at 30 °C for 2 days (passage 1). This procedure was repeated twice (passage 2 and 3). (a) Cells from passage 1 were used to prepare DNA and telomere length measurements were performed by telomere-PCR using specific primers amplifying either the 7L or the 6R-derived telomeres. Median telomere length is shown. Error bars correspond to SD. Adjusted p-values were obtained by the Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a false discovery rate correction **p < 0.01 (n = 14, 14, 16 and 9, respectively). Plates were scanned at high resolution (b) and analyzed to obtain a numerical value for each serial dilution set that is related to the intensity of the spots (c). Adjusted p-values were obtained by the Wilcoxon rank-sum test with a false discovery rate correction *p-value < 0.05, **p-value < 0.01 and ***p-value < 0,001. n = 16 for 7L-CTL, 6R-CTL and 6R-VST, n = 15 for 7L-VST. See Supplementary Table 3 for detailed p-values.