Figure 1.
Two X chromosomes Modulate the Transcriptome, Cellular Growth, and Pluripotency Exit in Mouse iPSCs
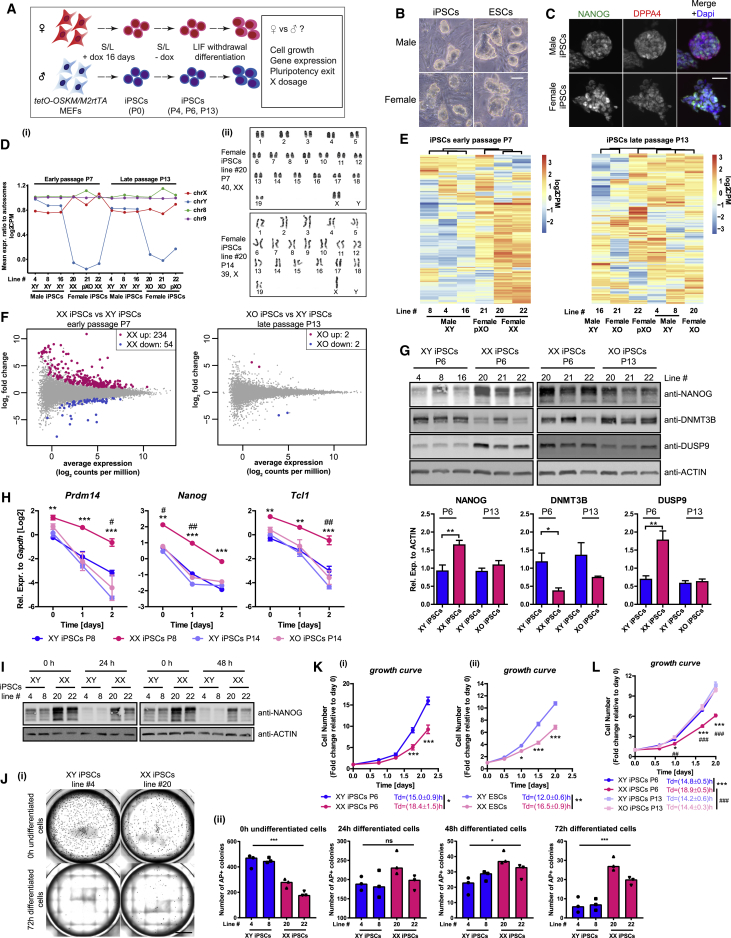
(A) Scheme of female and male iPSCs derivation, characterization, and differentiation.
(B) Representative images of female and male iPSCs/ESCs grown on feeders in S/L. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(C) Immunofluorescence analysis for NANOG/DPPA4 in iPSCs grown in S/L. Representative images of all lines examined for NANOG (red), DPPA4 (green), and DAPI (blue, nuclei counterstaining) are shown. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(D) (i) Mean expression ratio to autosomes for sex chromosomes and chromosomes 8 and 9. The dosage of X- and Y-linked genes was used to infer XX, XY, XO, and partial XO (pXO) genotypes. (ii) Representative karyotype images of XX and XO iPSC lines grown in S/L.
(E) Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of top 200 most variable autosomal genes in XY, XX, pXO, and XO iPSCs. Early-passage iPSCs cluster by X-dosage, late-passage iPSCs do not.
(F) DEG analysis, identifying clear differences between XX and XY iPSCs, but not XO and XY iPSCs (log2fold ≥ log21.5, FDR ≤ 0.05).
(G) Western blot analysis for NANOG, DNMT3B, and DUSP9 protein in iPSCs grown in S/L. Lower panel: quantification using actin as a loading control. Statistical significance was analyzed using unpaired two-tailed t test. P6, 6 XY versus 6 XX iPSC lines. P13, 3 XY versus 3 XO iPSC lines (n = 1).
(H) qRT-PCR analysis for pluripotency-associated gene expression during LIF withdrawal differentiation of both early- and late-passage iPSCs. Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post tests. P8, 3 XX versus 3 XY iPSC lines. P14, 3 XO versus 3 XY iPSC lines (n = 1).
(I) Western blot analysis for NANOG during pluripotency exit. The time after LIF withdrawal is indicated (n = 1).
(J) Two XX and 2 XY iPSC lines were subject to 0, 24, 48, and 72 hr of LIF withdrawal before replating 5,000 cells/well on feeders in 12-well plates. After 5 days in 2i/L, (i) representative images of alkaline phosphatase-positive (AP+) colonies for replated XX and XY iPSCs are shown (scale bar, 5,000 μm) and (ii) the number of AP+ colonies is indicated. Results are presented as averages (±SEM) of triplicates for each cell line (n = 1). One-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test.
(K) Growth curves and doubling times of XX and XY iPSCs (i) and ESCs (ii) in S/L condition. Cells were counted at the indicated time points and presented as fold changes relative to day 0. P6, 3 XY versus 3 XX iPSC lines (n = 1, left panel); 1 XY versus 1 XX ESC line (n = 3, right panel). Growth curve: two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post tests. Doubling time (Td): unpaired two-tailed t test.
(L) As in (K) but for XY, XX, and XO iPSCs (three lines each, n = 1).
Growth curve: two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post tests. Td: unpaired two-tailed t test.
P6 XX versus P6 XY iPSCs: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; P6 XX versus P13 XO iPSCs: #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001.
See also Figure S1.