Fig. 3.
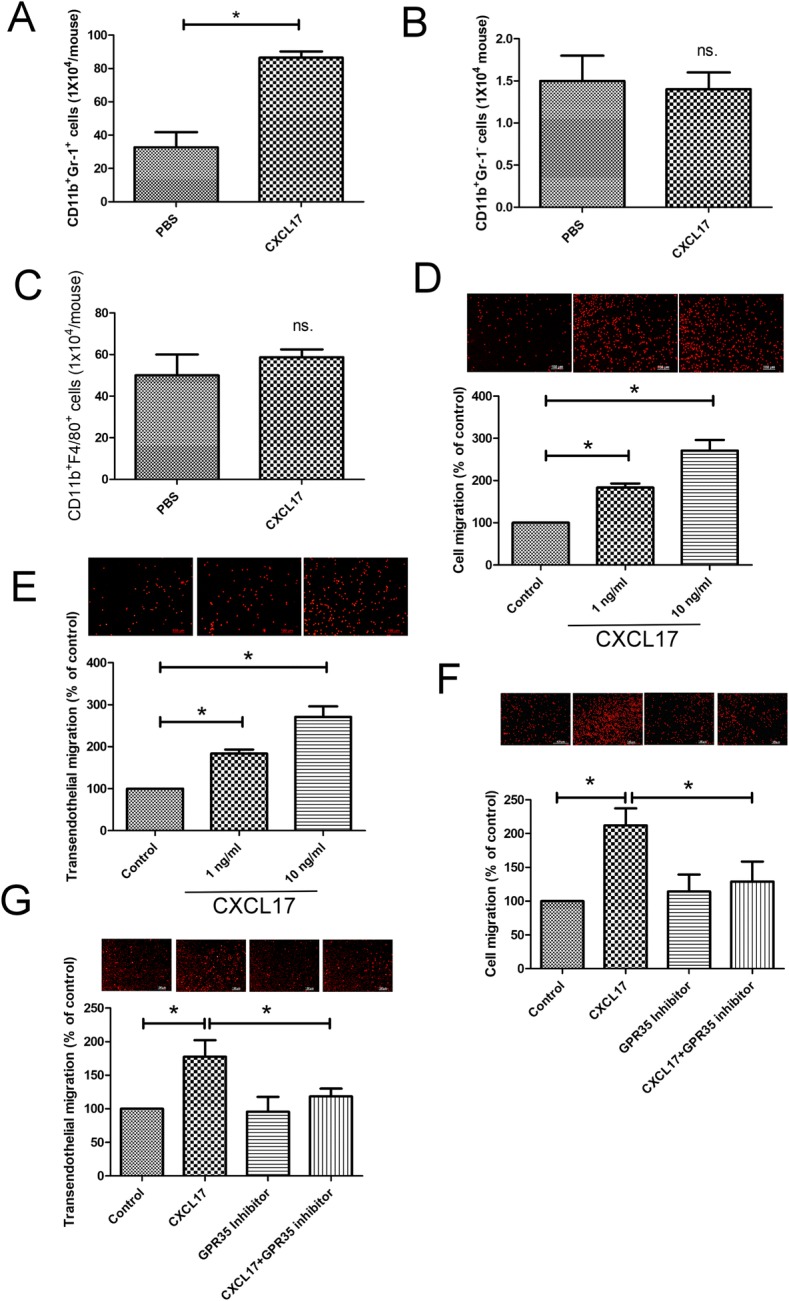
CXCL17 increases the recruitment of MDSCs in metastatic lungs of mice. The effect of CXCL17 in the recruitment of CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs (a), CD11b+Gr-1−MDSCs (b), and CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages (c) in the lungs of mice. BALB/c mice were treated with PBS or recombinant mouse CXCL17 protein by intra-tracheal administration for 14 days (1 μg/mouse, 2 times/week, n = 6 per group). Various immune cells were isolated from the lungs of mice by antibody conjugated magnetic beads. Each value is the mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05. CXCL17 increased the migration (d) and transendothelial migration (e) of CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs in vitro. GPR35 inhibitor decreased the migration (f) and transendothelial migration (g) of CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs induced by CXCL17. CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs were isolated from the lungs of normal mice (n = 3). PKH26-labeled CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs cells were seeded onto inserts (1 × 105 cells in 3-μm pore insert for migration analysis). For transendothelial migration analysis, C166 cells were seeded in 3-μm pore collagen-coated inserts for confluent monolayer, and PKH26-labeled CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs cells (1 × 105/insert) were seeded onto C166 confluent monolayer inserts, and the migration of cancer cells was assessed by fluorescence microscope. CXCL17 (1 ng/ml) were added in bottom well as chemoattractant. For blocking experiment, GPR35 inhibitor (CID2745687, 2 μM) was added in the inserts. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments, and each value is the mean ± SD of three determinations. *Significant difference between the two test groups (p < 0.05)
