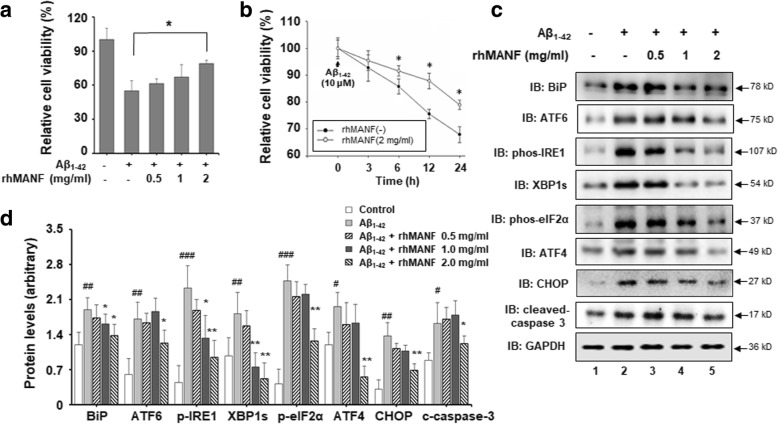
Fig. 5.
Recombination human MANF protein (rhMANF) protects against Aβ1–42-induced cell toxicity. a The dose-dependent effect of rhMANF on cell viability in the presence of Aβ1–42 exposure. SH-SY5Y cells were pretreated with different concentrations of rhMANF protein (0.5, 1, and 2.0 mg/ml) for 4 h prior to the Aβ1–42 (10 μM) treatment for additional 24 h and processed for the MTT assay. *P < 0.05, compared with the cells only treated with Aβ1–42. b The time-course of rhMANF on cell viability in the presence of Aβ1–42. SH-SY5Y were pretreated with rhMANF (2.0 mg/ml) for 4 h following the Aβ1–42 (10 μM) treatment for indicated times and processed for the MTT assay. *P < 0.05, compared with the only Aβ1–42-treated cells at indicated time points. c The protein levels of BiP, ATF6, phospho-IRE1, XBP1s, phospho-eIF2α, ATF4, CHOP, and cleaved caspase-3 were determined in SH-SY5Y cells treated with Aβ1–42 (10 μM) for 24 h with or without rhMANF. GAPDH was used as a loading control. d The densitometric quantitation of indicated proteins normalized to GAPDH levels in c. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with the cells only treated with Aβ1–42. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, compared with control group. All the quantitative data were presented as mean + SD of at least three independent experiments. C-caspase-3 cleaved caspase-3