Fig. 3.
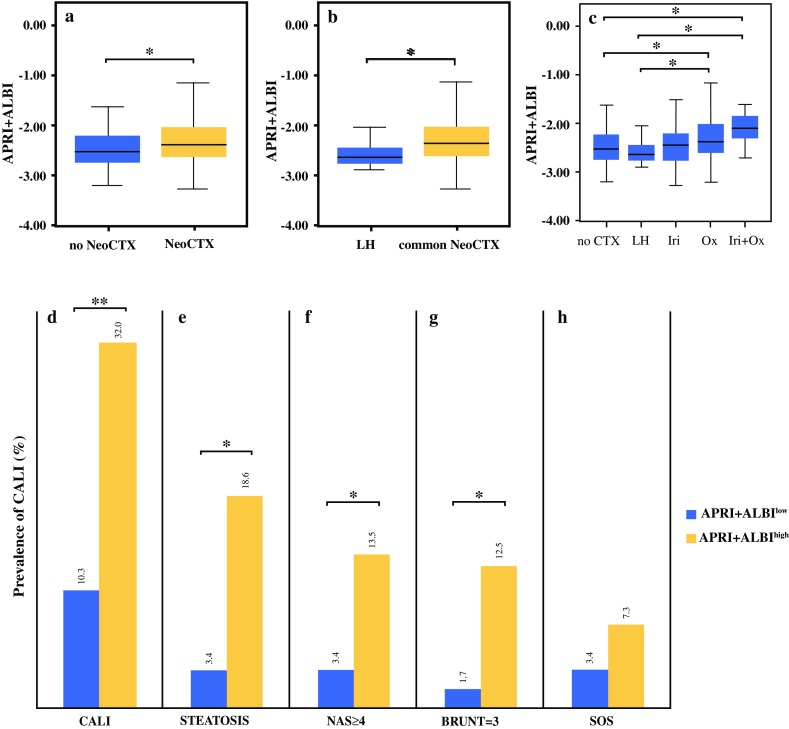
Patients above the proposed cutoff of – 2.46 for APRI + ALBI show a higher prevalence of chemotherapy-associated liver injury (CALI). Levels of APRI + ALBI are shown for patients who were or were not treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NeoCTx). Patients with (a) less hepatotoxic chemotherapy (for detailed information refer to Table S1) compared with (b) more hepatotoxic (irinotecan/oxaliplatin-based) NeoCTx, and (c) according to the type of NeoCTx. Furthermore, prevalence of (d) CALI, (e) steatosis, (f) chemotherapy-associated steatohepatitis according to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score (NAS) and Brunt et al.40, and (g) sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS) are shown for patients with high or low values of preoperative APRI + ALBI. APRI, aspartate aminotransferase (AST)-to-platelet ratio index; ALBI, albumin-bilirubin grade; LH, less hepatotoxic chemotherapeutic regimens; Iri, irinotecan; Ox, oxaliplatin. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.005
