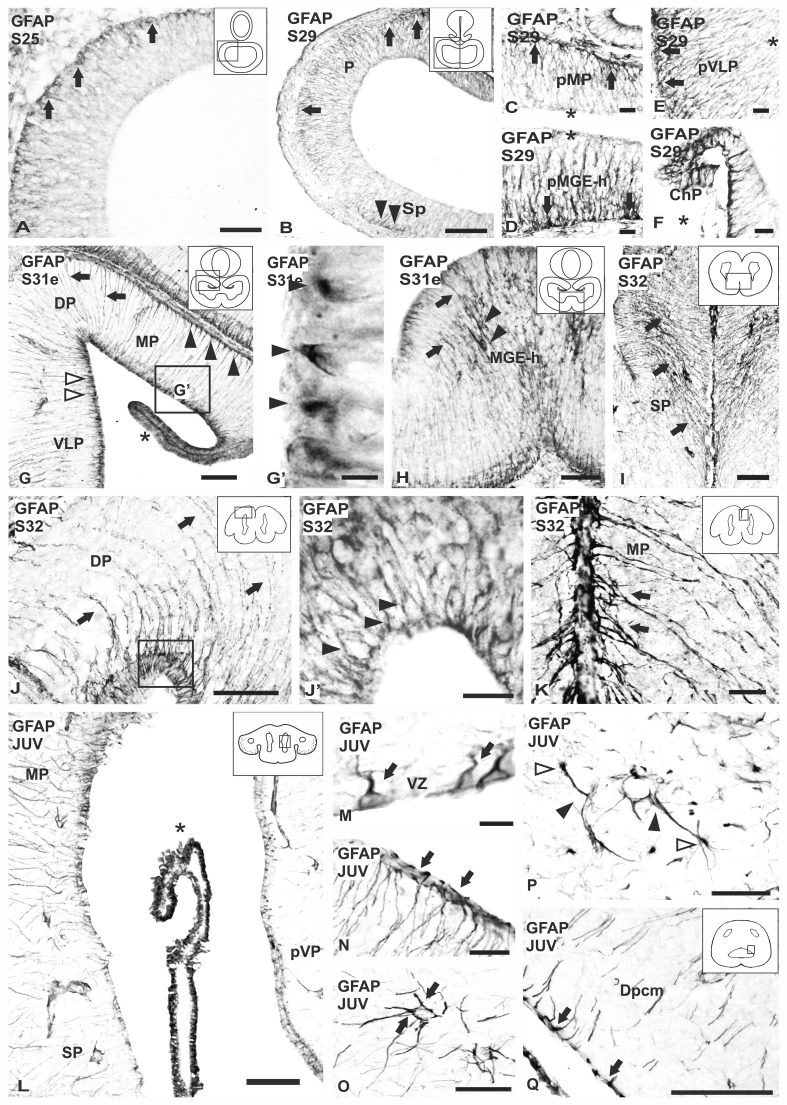
Fig. 4.
Photomicrographs of transverse sections of the telencephalon of S. canicula showing the expression pattern of GFAP in embryos (a–k) and juveniles (l–q). a Section of the telencephalon of a S25 embryo showing GFAP immunoreactivity in numerous endfeet in the pial surface of pallium (arrows). b–f Photomicrographs of a S29 embryo. b Photomicrograph at lower magnification showing GFAP immunoreactivity in radial processes extending from the ventricular surface to the pia in the pallium (arrows) and subpallium (arrowheads). c–e Photomicrographs at higher magnification showing an intense GFAP immunolabelling in the midline of the telencephalon (arrows) (c, d), in contrast to the rest of the telencephalon which shows weak immunoreactivity (arrows) (e). f Photomicrograph at higher magnification of the choroid plexus which show an intense GFAP immunoreactivity. g, h Photomicrographs from a S31 embryo at different magnifications. g Transverse section of the telencephalon showing radial processes (arrows), endfeet (arrowheads) and numerous positive cells lining the ventricular zone (empty arrowheads) positive for GFAP. Note the intense immunoreactivity in the choroid plexus (asterisk). g′ Photomicrograph at higher magnification of the ventricular surface showing the basal portion of cells close to the ventricle (arrowheads) immunoreactive to GFAP. h Transverse section of the subpallial midline showing intense immunoreactivity for GFAP at the ventricular and pial zone and numerous radial processes positive for GFAP (arrows); cells GFAP positive are intermingled between radial processes (arrowheads). i–k Photomicrographs from S32 embryos. i Section of the rostral telencephalon showing intense convergent processes (arrows) in the midline of subpallium. j–j′ Photomicrographs at different magnifications of the dorsal pallium showing curvy radial processes (arrows) and numerous cells in the ventricular zone showing GFAP immunoreactivity in the periphery of the cell body (arrowheads in j′). k Photomicrograph at high magnification of the medial pallium showing intense GFAP positive radial processes converging in the pallial midline (arrows). l–q Transverse sections of GFAP immunoreactivity in the telencephalon of juveniles. l Panoramic view of the ventricular zone of the telencephalon showing differences in the expression of GFAP between medial pallium, presumptive ventral pallium and subpallium. Note strong immunoreactivity in the choroid plexus (asterisk). m–o Magnifications of the ventricular zone, pial surface and blood vessels, respectively, showing ventricular positive cells (arrows in m), endfeet in the pial surface (arrows in n) and endfeet around blood vessels (arrows in o). p, q Details of the caudal telencephalon showing the presence of small cells close to blood vessels (empty arrowheads) and endfeet positive for GFAP surrounding blood vessels (arrowheads in p), as well as the presence of numerous endfeet in the roof of the caudal ventricle (arrows in q). Scale bars 200 µm (o), 100 µm (b, g, i, j, p), 50 µM (a, h, j′, m, n, q), 20 µM (c, d, e, f, k), 10 µM (g′, l)