Fig. 6.
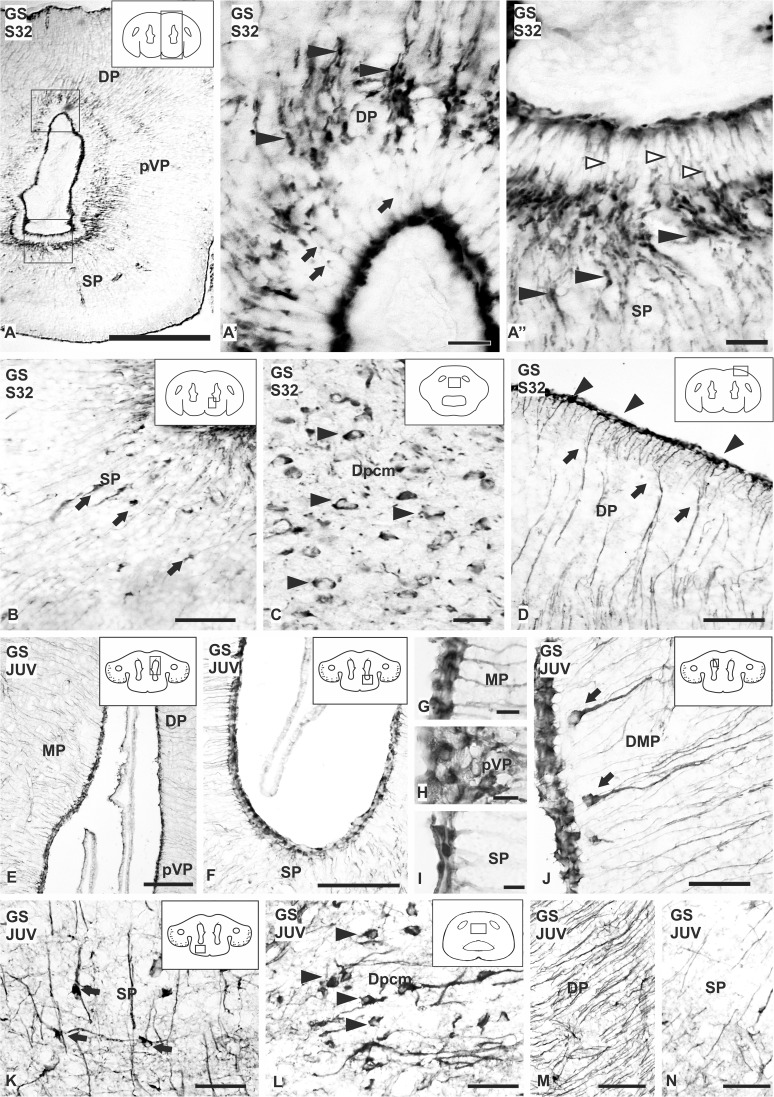
Photomicrographs of different sections of the telencephalon of Scyliorhinus canicula showing the expression pattern of GS during development (a–d) and juveniles (e–n). a Panoramic view of a transverse section of the telencephalon of a S32 of development showing GS immunolabeling. GS positive cells are mainly restricted to the ventricular zone, both in pallium (arrows) (a′) and subpallium (empty arrowheads) (a′′). Dilatations are pointed with arrowheads in a′–a′′. b Disperse GS positive cells are present in the subpallium near to the ventricular zone (arrows) and large cells are observed in the caudal dorsal pallium pars centromedialis (arrowheads) (c). d Photomicrograph showing radial processes (arrows) projecting to the pial surface, where they ramify and finish in endfeet (arrowheads). e–n Transverse sections of the telencephalon of catshark showing immunoreactivity for GS in the ventricular cells in pallium (e) and subpallium (f). g–i Details of the ventricular zone of the telencephalon at different levels showing GS positive cells. j Transverse section of the pallial ventricle showing paraventricular radial cells with a long basal prolongation (arrows). k, l Photomicrographs of disperse cells in the subpallium (arrows) and in the caudal telencephalon (arrowheads), respectively, immunoreactive for GS. m, n Transverse sections of the telencephalon showing differences in the amount of immunoreactive processes between pallium (m) and subpallium (n). Scale bars: 500 µm (a), 200 µm (e, f), 100 µm (b), 50 µm (d, j–n), 20 µm (a′, a′′, c), 10 µm (g–i)