Figure 1.
Characterization of PNF-Derived iPSC Lines
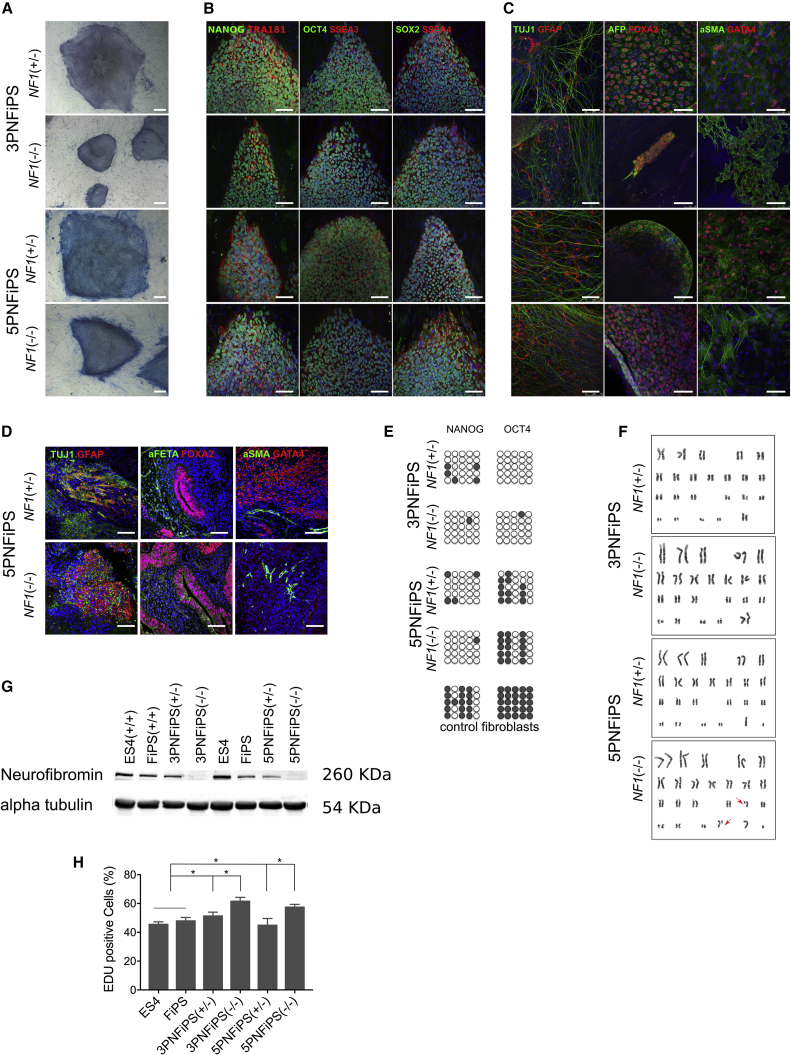
(A) Morphology and alkaline phosphatase staining of 3PNF and 5PNF iPSC colonies. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(B) Characterization of pluripotency markers. Representative images of 3PNF and 5PNF iPSC colonies stained positive for the pluripotency-associated markers NANOG, OCT4, and SOX2 (in green), and TRA-1-81, SSEA3, and SSEA4 (in red). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(C) In vitro differentiation potential of 3PNF and 5PNF iPSC lines. Generation of cell derivatives of the three primary germ layers including ectoderm (TUJ1 in green and GFAP in red), endoderm (AFP in green and FOXA2 in red) and mesoderm (SMA in green and GATA4 in red). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(D) Teratoma formation from 5PNF iPSC, showing their differentiation toward ectoderm (TUJ1 in green and GFAP in red), endoderm (AFP in green and FOXA2 in red) and mesoderm (SMA in green and GATA4 in red). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(E) Bisulphite sequencing showing demethylation of NANOG and POU5F1 promoters in the 3PNF and 5PNF iPSC lines.
(F) Karyotype of 3PNF and 5PNF iPSC lines at passage 20.
(G) Western blot analysis showing the absence of neurofibromin in 3PNFiPS(−/−) and 5PNFiPS(−/−). The human embryonic stem cell (hESC) line ES4 and a control iPSC line generated from foreskin fibroblasts (FiPS), both NF1(+/+), were used as control cell lines.
(H) Proliferation capacity of 3PNF and 5PNF iPSC lines assessed by Click-iT EdU Flow Cytometry Assay. Double-positive cells (in S phase) are represented in the graph. Bars represent means from three independent experiments.∗p < 0.05 (unpaired t tests).