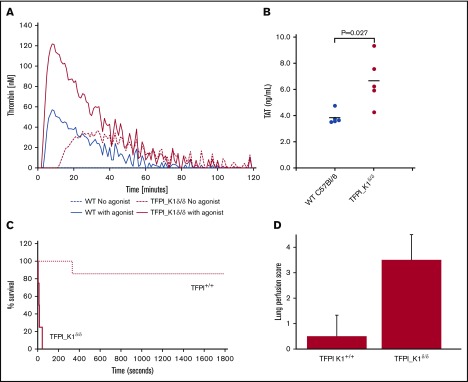
Figure 4.
Evidence of prothrombotic tendency of TFPI_K1δ/δmice. (A) Plasma from TFPI_K1δ/δ mice supports significantly enhanced thrombin generation as compared with plasma from WT C57Bl/6 mice. Thrombin generation assays conducted using TF as a trigger are shown for WT (blue solid line) and TFPI_K1–deficient plasma (red solid line). Background thrombin generation was observed in the absence of any added trigger in TFPI_K1–deficient (red dashed line), but not in WT plasma (blue dashed line). (B) Plasma TAT complex is elevated in TFPI_K1δ/δ mice compared with WT controls. TAT levels in TFPI K1–deficient and WT plasma were measured to be 3.8 ± 0.5 ng/mL vs 6.7 ± 1.9 ng/mL; mean ± standard deviation; P = .027. (C) Percent of surviving TFPI_K1δ/δ mice (solid line) and WT (TFPI_K1+/+) controls (dotted line) over time after IV injection of TF is shown. TFPI_K1δ/δ mice are more susceptible to TF-induced pulmonary embolism as compared with controls (P = .006 at 30 minutes). (D) Lung perfusion scores (arbitrary units) with Evan’s blue for TFPI_K1δ/δ and control mice following TF injection are shown. TFPI_K1δ/δ mice have significantly increased scores indicating increased perfusion defect (P = .003).