Figure 1. Expansion microscopy (ExM) concept and example outcomes.
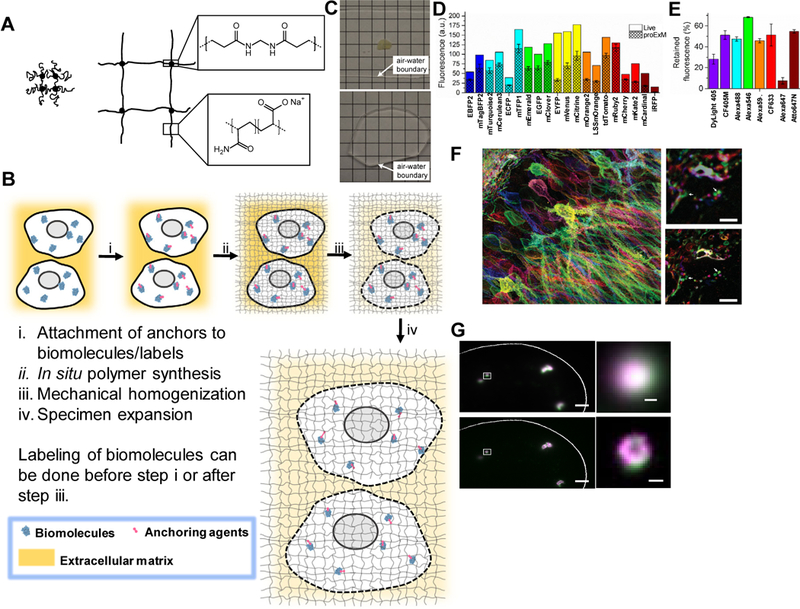
(A) Schematic of the ExM polyelectrolyte hydrogel, crosslinked sodium polyacrylate, showing the crosslinker (dot) and polymer chain (line), in the collapsed state before expansion (left) and in the expanded state after water dialysis (right). Insets show chemical structures of cross-linker and monomer components, in the synthesized polymer context. Adapted from ref. 5. (B) Diagram showing generalized workflow for ExM which involves (i) modification of biomolecules or labels (e.g., fluorescent antibodies) within a sample with a gel anchorable moiety (pink), (ii) in situ formation of the ExM polymer throughout the specimen, (iii) mechanical homogenization of the sample via heat treatment, detergent application, and/or enzymatic digestion, followed by (iv) expansion of the sample in water. Not to scale (the polymer spacing, or mesh size, is approximately 1–2 nm). (C) A 200 μm thick fixed mouse brain slice is opaque due to scattering before expansion (top) but is rendered transparent post-ExM, due to 100x dilution of the specimen contents in water (bottom). Adapted from ref. 5. (D-E) Retention of fluorescent proteins and antibody fluorescence in proExM. (D) Literature values of brightness for fluorescent proteins normalized to EGFP (open bars), compared to literature values of brightness multiplied by the observed retention percentage of each fluorescent protein with proExM (crosshatched bars, mean ± s.d.; n = 4 samples). (E) Retention of fluorescence of dyes conjugated to antibodies, after proExM (mean ± s.d., n = 3 samples). Adapted from ref.9. (F) Nanoscale imaging of intact brain circuitry with proExM. Shown is a specimen of mouse hippocampus expressing virally delivered Brainbow3.0 epitopes, stained with fluorescent antibodies, and then expanded via proExM (left); image shows maximum intensity projection of a high-resolution confocal microscopy stack. (Top, right), pre-expansion image of the boxed region of the left image. Arrows indicate features highlighted in the bottom, right image. (Bottom, right), post-expansion image of the top, right image. Adapted from ref. 9. (G) smFISH image before expansion (top panel) and post-expansion image processed with the ExFISH protocol (bottom panel), of NEAT1 lncRNA in the nucleus of a HeLa cell. Magenta and green indicate probesets binding to different parts of NEAT1. Right, a NEAT1 cluster (corresponding to the boxed regions of images on the left) imaged with smFISH (upper right) and ExFISH (bottom right). Adapted from ref. 10. Scale bars, (F, left) 50 μm (physical size post-expansion, 198 μm), (F, top right) 5 μm; (F, bottom right) 5 μm (19.8 μm); (G, top left) 2 μm; (G, bottom left) 2 μm (6.6 μm); (G, top right) 200 nm; (G, bottom right) 200 nm (660nm).
