Fig 3. Sirt5 KO induces increased lysine succinylation and decreased ATP synthase activity in mouse heart mitochondria.
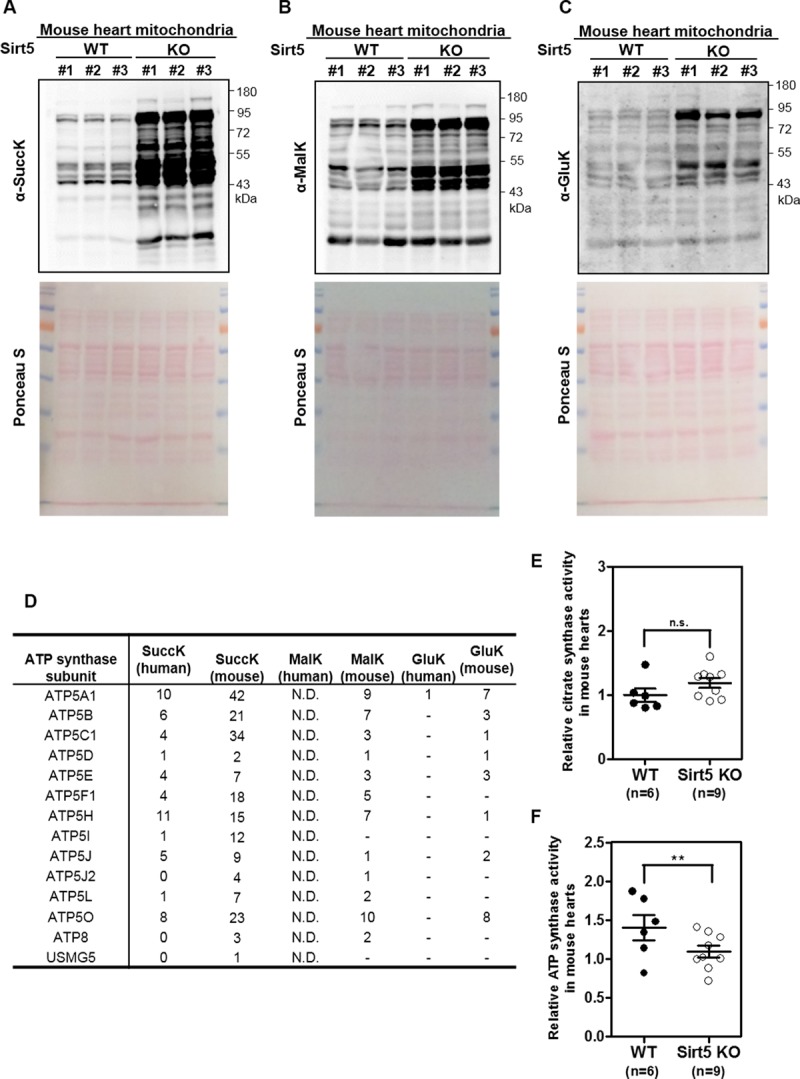
(A-C) Lysine succinylation, malonylation and glutarylation are dramatically increased in mitochondria of Sirt5 KO mouse heart. Male Sirt5 KO mice (n = 3) and WT control mice (n = 3) (16–28 weeks old) were fasted overnight. Upon sacrifice, mouse hearts were harvested for isolation of cardiac mitochondria. Immunoblotting was performed using the anti-sucinyllysine antibody (A), anti-malonyllysine antibody (B), and anti-glutaryllysine antibody (C). Total protein loading was stained with Ponceau S. (D) Summary of previous proteomic studies identifying ATP synthase subunits as succinylation/malonylation/glutarylation substrates regulated by SIRT5. The numbers of lysine sites which are regulated by succinylation, malonylation, glutarylation and SIRT5 were listed. N.D. = not determined. (E-F) Sirt5 deficiency inhibits ATP synthase activity in hearts of fasted mice. Sirt5 KO mice (n = 9) and sex-matched WT control mice (n = 6) (16–28 weeks old) were fasted overnight. Upon sacrifice, mouse hearts were harvested for isolation of cardiac mitochondrion, and were then subjected to citrate synthase activity (E) and ATP synthase activity (F) assays as described in ‘Materials and Methods’. Data are shown as mean ± SD of at least 3 independent experiments, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. **denotes the P < 0.01 for the indicated comparison. n.s. = not significant.
