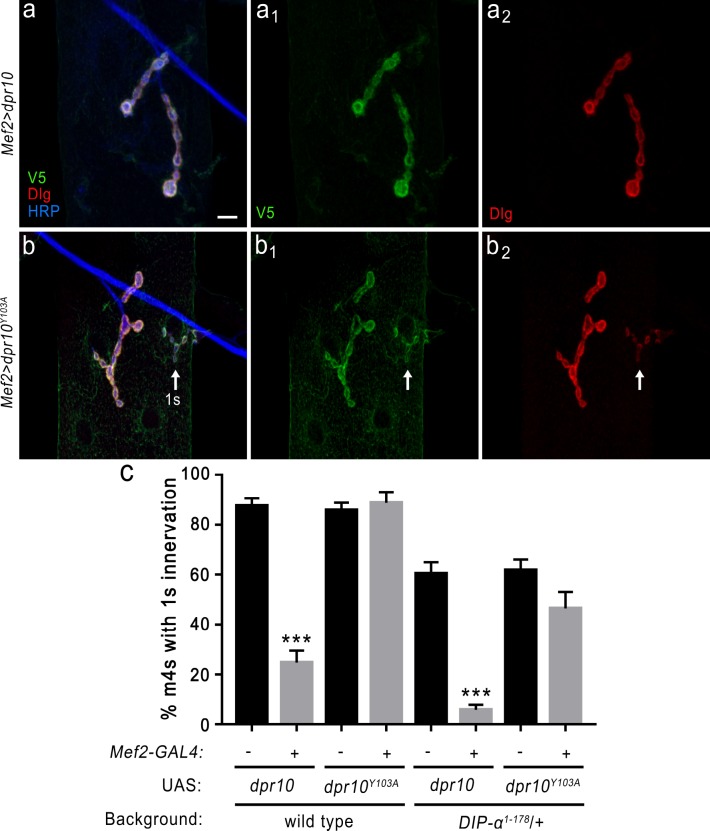
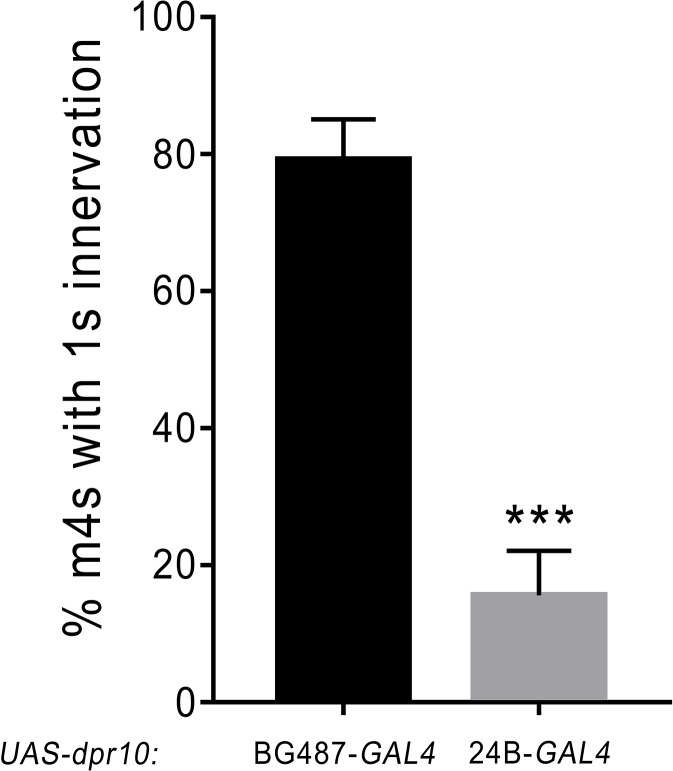
Figure 8. DIP-α is required for the loss of MNISN-1s innervation of m4 when overexpressing Dpr10 postsynaptically.
(a) Loss of MNISN-1s innervation of m4 due to overexpression of UAS-dpr10-V5 (referred to in the figure as UAS-dpr10) in muscles with the Mef2-GAL4 driver. Dpr10 is localized specifically to the postsynaptic membrane (green) and co-localizes with Dlg, a postsynaptic membrane marker (red). Anti-HRP (blue) labels all neuronal membrane. (a1) and (a2) show the individual Dpr10 and Dlg channels, respectively. Note that only 1b terminals are present. Also, the Dpr10 protein is labeled with anti-V5. (b) Muscle overexpression of a Dpr10 variant (UAS-dpr10Y103A) that is incapable of binding DIP-α does not affect m4 innervation. Both 1b and 1 s (arrow) terminals are present on m4. The 1b and 1 s terminals are easily distinguished by size and staining intensity of Dlg (b2) (see Materials and methods). (c) Quantification of 1 s innervation of m4. Overexpression of wild type UAS-dpr10 transgene results in 25% of m4s innervated by MNISN-1s compared to 89% innervation when overexpressing UAS-dpr10Y103A which is unable to bind DIP-α. n: See Figure 8—source data 1. ***p<0.0001. Calibration bar, 10 μm.