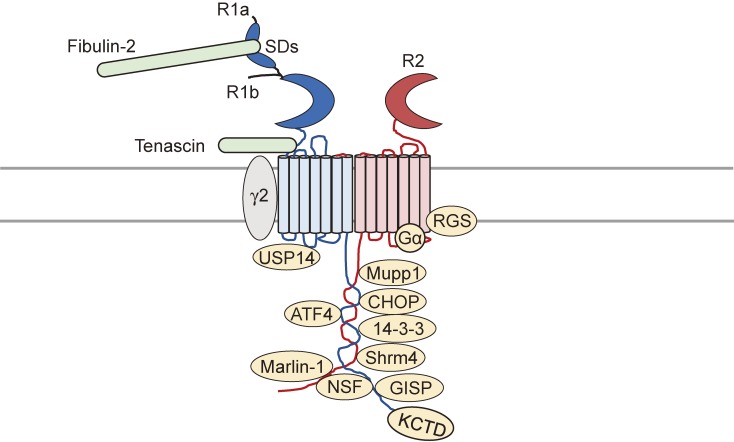
Figure 2.
GABAB receptor interacting proteins. A number of proteins have been found to interact with the C-terminus of GABAB receptor subunits. Among the interacting proteins are leucine-zipper transcription factors ATF4/CREB2 and CHOP, scaffolding and adaptor proteins 14-3-3, GISP, NSF, and PDZ domain-containing scaffold proteins Shrm4 and Mupp1. It is proposed that these proteins regulate receptor dimerization, intracellular trafficking, and synaptic localization. The C-terminus of the R2 subunit associates with KCTD proteins, which regulate CaV channel activity and GABAB receptor trafficking. The C-terminus of the R1 subunit associates with the brain-specific RNA binding protein Marlin-1 to target the cytoskeleton and regulate receptor transportation. Neurotransmitter receptors such as GABAA receptor γ2 subunit, mGluRs, and GIRK channels are also GABAB receptor binding partners although only the γ2 subunit has been identified to directly associate with R1 subunits so far. The N-terminus of R1 subunits also interact with proteins such as extracellular matrix protein fibulin-2 and tenascin. The extracellular sushi domains of the R1 subunit interact with fibulin-2, whereas tenascin binds to the extracellular domains of R1 subunits, possibly via the second transmembrane domain. Other proteins such as Gi/o proteins and RGS proteins bind to the R2 subunit to induce GPCR signaling.